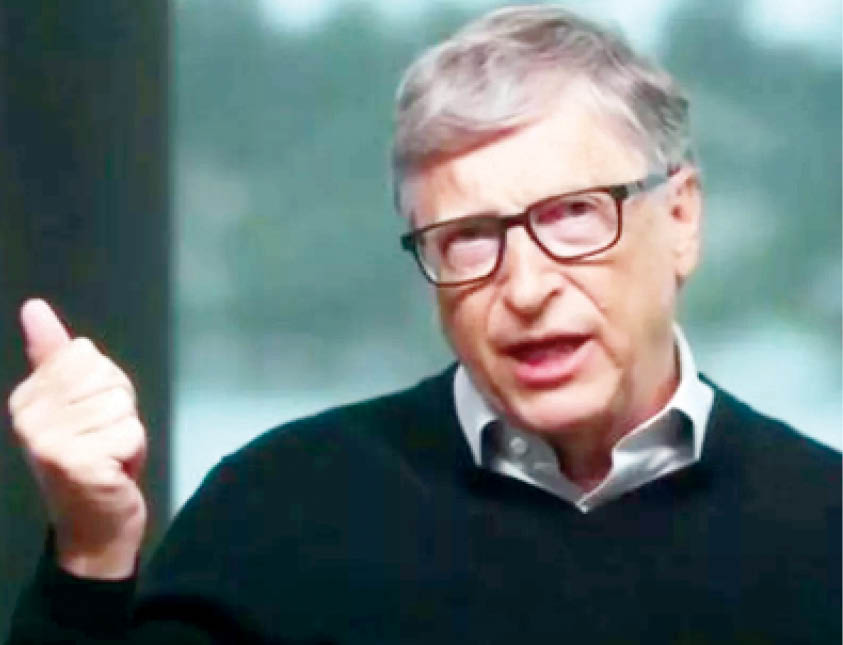
Mr Bill Gates has through the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation committed at least $1.75 billion to the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In this interview with selected journalists from across Africa, the billionaire, who stepped down as chairman of Microsoft Corp in 2014, shares insights on the impact of COVID-19 on the world, the current status of the global fight against the virus and how partners can support countries in Africa and elsewhere to ensure an equitable global response.
You’ve talked before about the dangers of a vaccine grab, and yet this is exactly what we’re seeing unfold. Could you share your assessment of the impact the rush for this vaccine is going to have on Africa?
Well, the key for the vaccines is getting more approved and getting more factories into production. A lot of the work that the foundation has done is to back a variety of vaccines. Back in 2015 in my TED talk, I talked about the risk of a pandemic, and how we weren’t prepared. At that time, not much was done. The foundation, Wellcome Trust, the UK, Japan and Norway did create a group called CEPI, which has helped a lot with a number of these vaccines.
With medicines, we always have this challenge with the big markets, the sales opportunities are in the rich countries. That’s why for diseases like HIV or malaria, the foundation reaches out to these companies and says, “We need to have some equitable approach.”
The first two vaccines that were approved are fairly costly to make and hard to scale up. They’re very good vaccines, Pfizer and Moderna, but it’s the next three, including AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson and Novavax that will give us the highest volumes, the ease of scaling and the thermal stability. And so, we’re hopeful that, particularly with some factories in India, that the foundation has helped to finance, which have larger factories than the factories in the West, within the next few months a large number of doses will come out of there and be targeted almost entirely at the developing world, which is the goal of what we call COVAX.
It’s a dynamic situation, I’ve been talking with governments and companies about this going back to last March, and so we have a chance here to get a lot of vaccines.
In Africa, the epidemic itself in a direct sense has been worse in South Africa. The rest of Africa, with a few exceptions, hasn’t been super bad. But of course, the economic effects are there and any life that’s lost is really terrible. So we need to first get the 20% coverage, and then move to 70 to 80% coverage and I’d say the foundation is at the forefront of that but it’s still unclear how well all these efforts will go.
Is there a plan for the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to assist poorer countries in developing COVID-19 vaccine production capacity?
There are a very high-volume of factories in the developing world, primarily in Indonesia and India. Making a new vaccine factory is a more than five-year effort.
Definitely, to be ready for the next pandemic, I think that there will be factories using this mRNA approach, that are put in multiple places in Africa so you’ll have guaranteed quick supply.
For this epidemic, we need to take advantage of the large capacity that people like Serum, BioE, and many others have, which are the developing world manufacturers who can in volume, make four to five times as many vaccines as all the Western companies put together.
So, the factories really are there. We can’t get new ones overnight but these highly scalable vaccine constructs, the next three, the numbers can be very large. As soon as that can happen, the best.
Until the vaccines reach everyone, new clusters of the disease will keep popping up. Last December, The Economist, projected that the vaccine will be widely available in Africa in 2022 or 2023. What can be done to improve the supply?
Well, the agreement we have with India is that those factories, at least half the capacity, will be dedicated to supply, through GAVI, to Africa and other developing countries. Every day, of course, we’re trying to speed this up. The history of vaccines is that until GAVI was created in the year 2000, the really key vaccines for saving literally millions of lives were not cheap enough for the poor countries, and the coverage levels were very low.
And so GAVI deserves more visibility for what it did, funded by many governments and our foundation, to get diarrhoea vaccines and pneumonia vaccines into all the children in the world. And so, the GAVI approach, where GAVI buys the vaccines at the very lowest price with that donor money, has worked very well. That’s why deaths of children under five, since the year 2000, in the world at large has been cut in half. It’s an even higher percentage if you just focus on Africa.
So, we have that success story. GAVI had a hard time getting money from the United States, until recently, which was fairly key, so both Melinda and I were working on that. We were successful in getting a $4 billion allocation for GAVI. In the meantime, we were giving money to get these factories ready.
So, the whole vaccine model that emerged on GAVI, that’s what we’re trying to use here.
Now, doing it very quickly is a challenge because you never want to build a factory that can’t make quality vaccines.
You really would prefer to use vaccines that have gone through the toughest regulatory process, like the US regulator or the UK regulator, and then receive the WHO blessing.
What would you have to say to those who are sceptical about taking any vaccine?
For people who care about childhood death, vaccines are the best thing that ever happened. Smallpox killed over a million people a year, and because of vaccines, now smallpox is gone. The miracle of vaccines is very clear. When a child dies, that’s a very clear thing. We have very good statistics on what that was like before we got these new vaccines.
Over 10 million children were dying under the age of five every year, with a high portion of those being in Africa.
The more people learn about vaccines, the more amazed they should be about how fantastic they are.
We are now getting the experience with these coronavirus vaccines; I had my first dose last week. There are very, very few side effects, and it is protecting people. In fact, almost no one who has been vaccinated has had severe disease, which is really quite miraculous.
I hope people will read the facts about vaccines, and how they’ve worked against other diseases, and see that now we have millions and millions of people who’ve taken this vaccine and we’re tracking that experience to make sure we were right about the overall safety. It is going to be a tragedy if a country continues to have an epidemic because of these false vaccine rumours.
Nigeria is planning to spend around a billion dollars in acquiring the vaccines but, since Nigeria has low infection rates, wouldn’t it be good if most of this money was put towards strengthening the health sector and just give vaccines to the vulnerable?
Well, there’s no doubt that the impact of putting money into the health system, particularly the primary health care system, will be very high in terms of saving children’s lives. And you’re absolutely right, Nigeria should not divert the very, very limited money that it has for health into trying to pay a high price for COVID-19 vaccines. The key is that Nigeria is still eligible, and so, for a lot of those vaccines, they will come through the GAVI facility that we’ve raised money for. Health in general in Nigeria is very underfunded.
If you look at the primary health care centres in the north and, in particular, if you look at the vaccine coverage rates, there are millions of lives that can be saved if the primary health care system operated at a level that some other countries with the same wealth as Nigeria. I’m an advocate for the government to have more resources and prioritise health. Obviously, I’m not a voter in Nigeria, so Nigeria can decide that independently. Waiting for the GAVI vaccines would be the best thing and to put into other areas so that vaccine coverage rates, that are as low as 20% in some areas, get up to 80/90% to save children’s lives.
Did you have a choice in the vaccine that you took? And secondly, I would like to know if your foundation funds anything to do with oxygen for COVID-19 in Africa?
So, in terms of that last part, our foundation has been very involved in planning a lot of emergency things, including getting drugs like dexamethasone available.
There’s also the African medical supplies effort, which we’re very supportive of, and it includes efforts to cause oxygen to be available, and I’m sure our office in Africa would be glad to follow up with more specifics of what we’ve done there on the work in diagnostics that we’ve supported, the African CDC which we’ve been a big supporter of and has done a good job, and the oxygen has been a very valuable thing.
I ended up getting the Moderna vaccine, I had no choice, they don’t ask what your preference is. There are only two vaccines approved in the United States right now, Pfizer and Moderna. They’re both very good vaccines and very safe.

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.