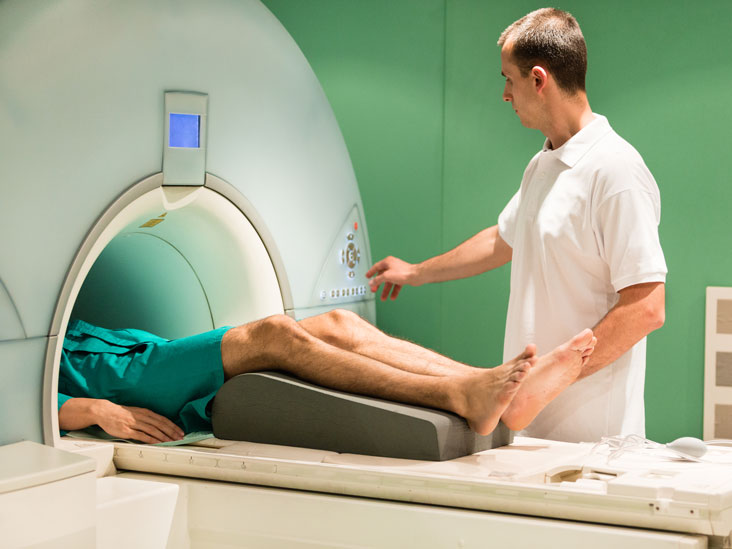
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) test is a diagnostic imaging modality used in examining the anatomy and pathologies in humans and to some extent veterinary medicine.
According to research, MRI has played an important role in confirming diagnosis, as well as evaluating the size and extent of the malformation when physical examinations tend to underestimate the major factors that are deeply seated on malformations without subcutaneous portions which may only be detectable in magnetic resonance. The test is carried out on patients with soft tissue injuries, pathologies and spinal injuries.
A radiographer, Mustapha Nganjwa, said MRI is a non-ionizing radiology technique that uses magnetism, radio waves and a computer to produce images of the body structures, based on the principle called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
He said the test is used for domestic and research activities and is advantageous over other imaging modalities. Hence the diagnostic uses are for finding unhealthy tissue in the body, locating tumor, and surgery planning. The research uses are for determining the relationship between images and disorders and understanding how the brain works during tasks.
Mustapha added, “This imaging test takes place on patients when plain X-ray and ultrasound scan result are inconclusive on the nature and degree of injury on a particular tissue or organ and the plain conventional X-ray could not give the required information about a particular case, then MRI will be required to give a better contrast and solution.”
He advised doctors to ensure patients undergo MRI suit devoid of any metallic objective within implant or outside the body irrespective of their health when carrying out an MRI test.
Also during the procedure, the doctor should ask the patient questions about their health status or their recent surgical history, metallic implant, victim of blast, pregnancy and other related issues with their health.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.