With less than two months to the expiration of this administration, Daily Trust on Sunday reports that President Muhammadu Buhari has failed to fulfil his major campaign promises on lifting millions of Nigerians out of poverty and creating 3 million jobs annually.
Available data from relevant institutions showed that more Nigerians have lost their jobs while others became poorer under the All Progressives Congress (APC)-led administration compared to how the situations were in 2015.
However, some observers noted that the President Buhari administration ought to have done better, but added that job losses and increased poverty were not limited to Nigeria.
They said that three major events that took the Buhari administration unawares included slump in oil prices from 2014 to 2017, which significantly reduced government revenues, leading to recession in 2016.
Party crisis: How PDP, APC national chairmen lost their seats since 1999
Interim government is a joke taken too far
They observed that the advent of COVID- 19 and its economic impacts in 2020 and 2021, resulting in another recession in 2021, had dealt a big blow on economies around the world, Nigeria inclusive.
They also said the ongoing economic impacts of the Russia-Ukraine war remained a stumbling block to the yearnings and aspirations of leaders around the world.
One of the observers said no government in Nigeria had ever suffered these three events concurrently. He added that these are all global economic events that impacted all countries negatively, particularly in Africa, saying Nigeria even fared better than other countries on the continent and beyond.
An economist, Baffa Usman, said while the outgoing administration would be excused for not fulfilling some of the promises it made, it would also not be forgiven for not doing better than what is on ground.
“The president has all the goodwill he needs to take radical decisions, but it appeared he thought eight years would not pass.
“He took too long to have his cabinet, and then, longer time without a potent economic team. Remember, they claimed to have created jobs through social works in all the 774 local government areas. Those so-called jobs have since fizzled out. They only gave bonuses to few individuals,” Usman said.
He said the real unemployment figures would be known in the next few months.
“So much damage has been inflicted on the economy through the cashless policy enforcement by Buhari at the twilight of his administration. Millions of people, especially petty traders whose capital base is less than N20,000 have been wiped out. They are now beggars,” he added.

Buhari’s dream for better Nigeria
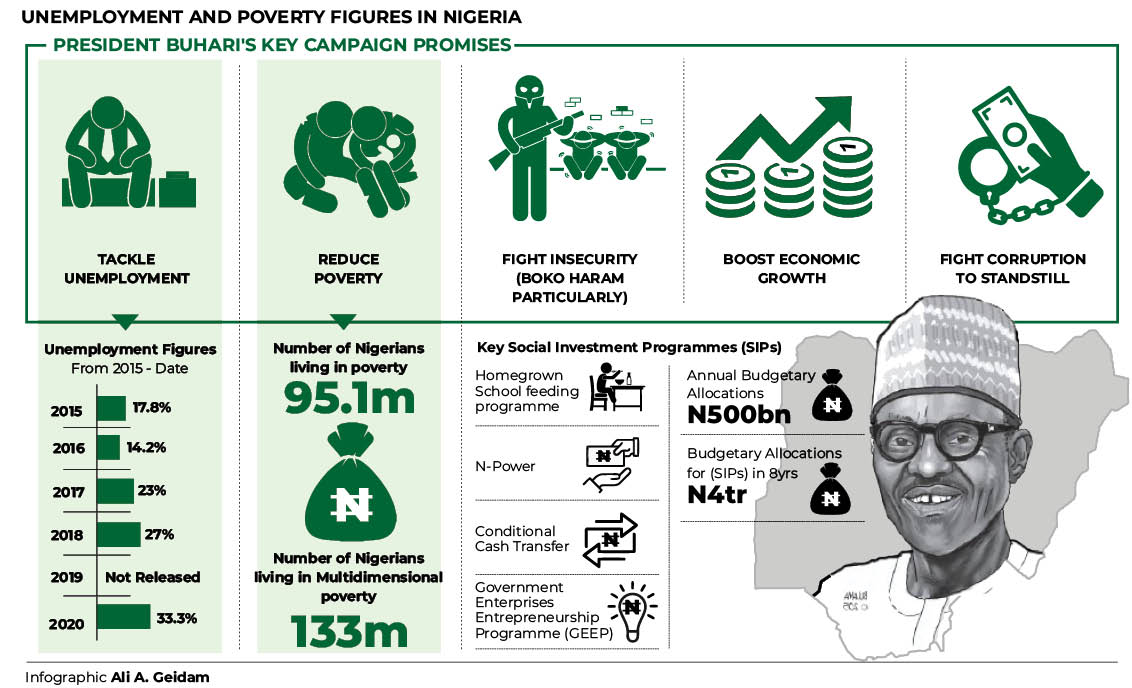
One of the president’s key campaign promises in 2015 was to tackle high unemployment rate and poverty in the country, partly by creating 3million jobs annually.
Assuming he has achieved this, the president would have created 24million jobs by now.
However, the current unemployment data and poverty level in the country have clearly shown that the government has failed to fulfill these two fundamental promises.
In his 2015 inauguration speech, the president said, “Unemployment, notably youth unemployment, features strongly in our party’s manifesto. We intend to attack the problem frontally through the revival of agriculture, solid minerals and mining, as well as credit to small and medium-size businesses to kick-start these enterprises.”
In their campaign manifesto before defeating former President Goodluck Jonathan and the then ruling Peoples Democratic Party (PDP), the APC had made several commitments to Nigerians, among them poverty reduction, tackling insecurity, improving employment, economic growth, as well as fighting corruption. For instance, during a Christmas message to Nigerians in December 2014, Lai Mohammed, the then national publicity secretary of the APC and now Minister of Information and Culture stated, “Our eight pledges for a better Nigeria, which are highlights of our manifesto, form the core of our social contract with Nigeria. During our first term in office, we pledge to create 3million new jobs a year through public works programmes; and shifting the economy towards value-added production will be our primary economic target.
“We will strengthen security by employing at least an extra 100,000 police officers and establishing a properly trained and equipped federal anti-terrorism multi-agency task force to destroy Boko Haram and any form of insurgency. We will also introduce an immediate pay rise and improved conditions for all five security services.
“To fight corruption, the cankerworm that has eaten deep into the fabric of our society, we will adopt a zero-tolerance approach to the vice – rooting out dishonest public servants and imposing tough sanctions, including jail sentences.
“To position our youth for better job opportunities, we will provide interest-free loans for university/technical school students who meet the required entry qualifications, and this will be funded by providing guarantees to the banking sector and by absorbing the interest. Also, we will introduce a free daily school meal for all children attending primary school.
“As a first phase to battling poverty, we will introduce direct conditional monthly social security payment for 25million of the poorest Nigerians.”
Our correspondent reports that while it is believed in some quarters that the government has done well in decimating the Boko Haram insurgency in the North East, new security threats, among them, the activities of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB) in the South East, increased oil theft in the South South that denied Nigeria serious income; banditry, accompanied with kidnapping in the North West, have collectively dwarfed the achievements recorded in the security sector.
Although some of these vices have been significantly reduced in the last few months, the dream of President Buhari to improve agriculture was also affected as millions of farmers could not access their farmlands for obvious reasons.
Unemployment figures
Checks by Daily Trust on Sunday showed that unemployment rate in the second quarter (Q2) 2015 when President Buhari took over power was 14.9 per cent, which translates to about 6.1million people as released by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). Fast forward to 2023, the figure has tripled as the current unemployment rate, according to the NBS, stands at 33.3 per cent, translating to about 23.18million jobless Nigerians.
Although the last unemployment data released by the NBS was in the fourth quarter of 2020, indicators are showing that the number of unemployed Nigerians is way beyond 23 million.
According to the NBS, the labour force population covers all persons aged 15 to 64, who are willing and able to work, regardless of whether or not they have jobs.
A breakdown of the unemployment figures by Daily Trust on Sunday shows that in the second quarter of 2015, unemployment between 18 and 64 age bracket was 14.9 per cent and later surged to 17.8 per cent in the third quarter.
In 2016, the unemployment rate was 12.9 per cent in Q1; 13.3 per cent in Q2; 13.9 per cent in Q3 and 14.2 per cent in Q4.
In 2017, the data showed 14.4 per cent in Q1; 16.2 per cent in Q2; 18.8 per cent in Q3 and 20.4 per cent in Q4.
Similarly, in 2018, data by the NBS showed 21.8 per cent in Q1; 22.7 per cent in Q2 and 23.1 per cent in Q3.
The Q4 unemployment report of 2018 was not released and the whole of 2019, as well as Q1 of 2020, until Q2 of 2020, where the data stood at 27.1 per cent, and Q4 of 2020, where the highest rate was 33.3 per cent.
The Minister of Labour and Employment, Chris Ngige, while defending the administration, said President Buhari created seven million jobs since assuming office in 2015 through one of the Social Investment Programmes (SIP), the N-Power programme, which began in 2016. The SIP formed one of the campaign promises of the APC.
The programme is divided into four major categories—Home Grown School Feeding Programme for public primary schools; Conditional Cash Transfer to less privileged; N-Power for unemployed graduates and Government Enterprises Entrepreneurship Programme (GEEP) to encourage market women, artisans and traders.
However, data made available by the NBS on job creation showed that 141,368 jobs were created in the Q2 of 2015, around the period when President Buhari assumed office and 475,180 jobs were created in Q3 of 2015. The total number of new employment recorded was 499,521 jobs.
In Q1 of 2016, the total number of jobs generated was 79,469. In Q2, the total number was 155,444. In Q3 of 2016, 187,226 jobs followed. This brings the total as at the Q3 of 2016 to 1,538,208. There are no NBS statistics for Q4 of 2016 and the Q1 of 2017 so far.
This puts to rest the claim by the minister that seven million jobs were created since 2015 as it was almost impossible.
According to the methodology provided by the NBS, the survey took into account the formal, informal and public sector jobs.
The claim, which was fact-checked, also showed that the minister’s statement about N-power creating “millions of jobs” is incorrect as the programme has only engaged 500,000 people. As such, the claim of creating seven million jobs claimed by Ngige cannot be substantiated, considering the figures by the NBS and the current state of the economy.
Poverty level on the rise
In the area of poverty alleviation, President Buhari had promised to lift 100million Nigerians out of poverty in 10 years, and in July 2021, he reiterated the commitment of his government to fulfill the promise.
President Buhari, in June 2021, set up a committee known as National Poverty Reduction with Growth Strategy (NPRGS), intended to carry out mandates that would lead to lifting 100million Nigerians out of poverty as promised.
Reiterating his commitment to fulfilling his promise, Buhari’s Senior Special Adviser on Media and Publicity, Garba Shehu, in a statement in July 2021 noted,
“I wish to restate my commitment that getting 100million Nigerians out of poverty is realisable.
“The country is robustly blessed with good weather conditions, good soil, human and material capacity and resilience to make a difference by all the hardworking youths.
“We can do it, and we will do it. No excuse will be good enough to remain a mono-economy with all the challenges in oil production and fluctuating global prices when we have vast opportunities in crop and livestock production.”
But the NBS recently announced that Nigeria had 133million people, representing 62.9 per cent of the population living in multidimensional poverty.
This, according to the NBS report, means that 133million Nigerians experienced deprivations in more than one dimensions, or in at least 26 per cent of weighted deprivations, adding that while 4 out of 10 Nigerians experience monetary deprivation, more than 6 out of 10 are multi-dimensionally poor.
The average deprivation score among poor people, which shows the intensity of poverty, is 40.9 per cent. Over a fifth of poor people experience deprivations in at least half of the dimensions or weighted indicators. The poorest districts also have the highest intensity of poverty – each poor person is deprived in 51 per cent of the weighted MPI indicators in Kebbi South and Bayelsa West, the NBS added
It further stated that, “Seven out of 10 Nigerians living in the rural areas are multi-dimensionally poor compared to four out of 10 in urban areas. Multidimensional poverty is higher in rural areas, where 72.0 per cent of people are poor, compared to 42.0 per cent of people in urban areas. Approximately 70 per cent of Nigeria’s population live in rural areas, yet these areas are home to 80 per cent of poor people.
“The intensity of poverty in rural areas is also higher, at 41.9 per cent, compared to 36.9 per cent in urban areas.
Also, the World Bank has said that the number of poor Nigerians is projected to hit 95.1 million in 2022.
The bank made this known in its poverty assessment report titled, “A Better Future for All Nigerians: 2022 Nigeria Poverty Assessment.”
The report noted that COVID-19 crisis is driving up Nigeria’s poverty rate, pushing more than 5million additional people into poverty by 2022.
With real per capita growth being negative in all sectors in 2020, the bank said poverty was projected to have deepened for the current poor, while those households that were just above the poverty line prior to the COVID-19 crisis would be likely to fall into poverty.
“Were the crisis not to have hit (the counterfactual scenario), the poverty headcount rate would be forecast to remain virtually unchanged, with the number of poor people set to rise from 82.9 million in 2018/19 to 85.2 million in 2020 and 90.0 million in 2022, due largely to natural population growth,” the bank said.
Consequently, the federal government, in different for a, had said that the country budgeted N500billion annually for different social investment programmes.
No miracle in solving unemployment, poverty problems in 2months – Expert
A development expert and executive director, Centre for Transparency and Integrity Watch, Umar Yakubu, said the president could not redeem himself on the promises he made to Nigerians on poverty and unemployment within the two months left for him to go.
“When the president came on board, one of the things he said he would do was to lift 100million people out of poverty, now more people are in the poverty bracket. The social co-efficient index had widened as well (that is the gap between the reach and the poor).
“In the next two months, there is no miracle that can happen to make the poverty and unemployment index improve,” he said.
Yakubu added that to solve these challenges, Nigeria basically must fix its power infrastructure, reduce import and tackle insecurity to attract investors.
“Today, despite billions of dollars spent on the power sector, we barely manage to do 5,000 megawatts, which is not enough to drive industrialisation, especially in the area of agriculture, manufacturing, steel, among others.
“Also, our import bill is too high; when there is high import, it kills our local capacity. Although there is improvement in agriculture, we still import the basic things we could have easily produced. So the next government has to look at the issue of import.
“Similarly, access to finance is important. For instance, today, banks lend at double digits of up to 27 per cent interest and micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) can’t cope. Lastly, insecurity is key because any investor wants to come to secure environment to do business; and without such secured environment, no investor will come and invest, as well as create jobs.
“As such, with all these factors mentioned, there is no miracle the president can do to solve these unemployment challenges in two months,” he said.
You are not raising new issue – Presidency
Reacting, the Presidency said the report was not raising a new issue as the leading opposition political party, the PDP had said similar things.
The Senior Special Assistant to the President on Media and Publicity, Malam Garba Shehu, simply said, “The PDP has said this. You are not bringing up a new issue.”
Before his response, Daily Trust on Sunday had sent a questionnaire stating that a fact-checking report had showed that President Buhari had not fully fulfilled campaign promises on poverty reduction and unemployment barely two months to the end of his administration.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.

