In the middle of farmlands of about 1000 square metres is a white painted wall, enclosing the burial place of the 12th Sultan of Sokoto, Muhammad Attahiru I, who reigned from October 1902 to March 1903 when he was killed by British invaders in Mbormi. Daily Trust on Sunday visited the tomb site and reports how the historical monument has been neglected.
The tomb is located at a town called Mbormi, four kilometres from Bajoga, the headquarters of Funakaye Local Government Area of Gombe State, which is about 76 kilometres from Gombe, the capital of the state.
Mbormi is historic because in the 20th century, it had defensive walls and trenches where Sultan Attahiru stopped over on his way to the east, 118 years ago after he left Sokoto in protest over the invasion of the caliphate by British colonialists.
However, following the killing of the Sultan, alongside his two sons, chief imam and over 600 followers after a fierce battle with British forces, the town was completely razed and British authorities banned locals from erecting any structure at the site. As such, Mbormi is now desolate, apart from the three graves of Sultan Attahiru I, the chief imam of Sokoto and Major Francis Charles Marsh, who also died during the battle. The vast area is now farmlands for people of surrounding villages of Bula Gaidam and Garin Aba.

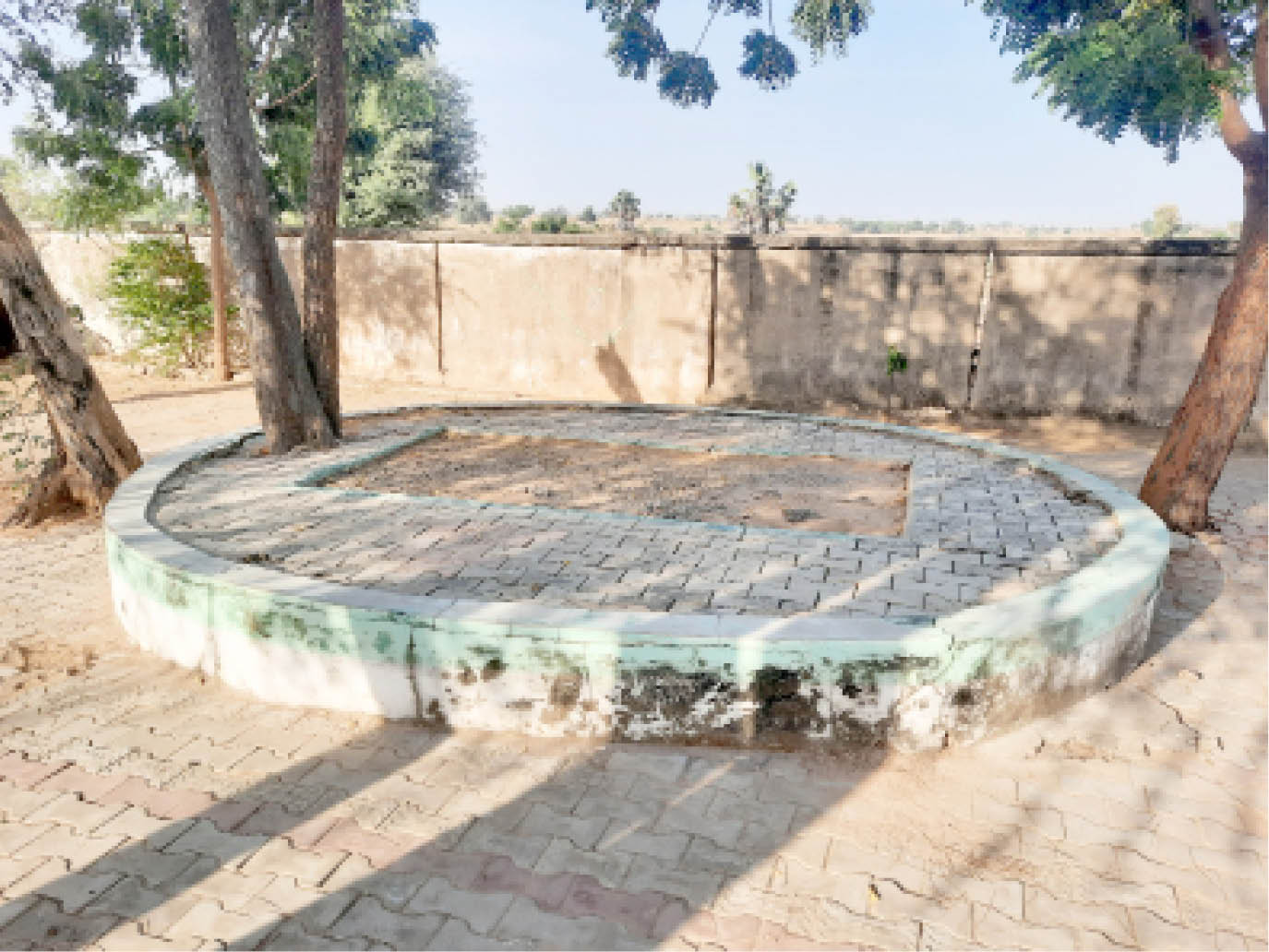
Our correspondent who visited Mbormi reports that apart from the wall that serves as fence for Sultan Attahiru’s tomb, there is virtually nothing to show that a tomb of a revered personality of his caliber is situated in that place.
The tomb site is located along a rural road leading to Ashaka town while the passageway to it is a bush path through vast farmlands of about 1000 square metres.
Both outside and inside the tomb are not looking impressive. It is underneath neem and desert date (aduwa) trees, with cemented blocks encircling it.
The wall fencing the area is just about five feet long; therefore, it is easy for passersby and even animals to enter the premises unhindered.
When our correspondent visited the place, there was no tour guide or security personnel. The entrance door was left open, unlike what is obtained at Shehu Hubbare in Sokoto, where Attahiru’s great grandfather, Sheikh Usman Ibn Fodiyo, was buried. Even the white paint on the fence has worn out as a result of years of neglect, with some parts on the verge of collapse.
After hours of waiting, an elderly man showed up about 12 noon and told Daily Trust on Sunday that he volunteered to look after the place and keep it clean on a daily basis, adding that he didn’t receive salaries or allowances from the government.
A man who gave his name as Ahmad Bello said that in the past, people within and outside the state visited the place in large numbers, especially on Mondays and Fridays, to offer prayer to the late Sultan or seek his blessings.
However, on that particular Monday, for the three hours our correspondent spent at the place, only few people visited; they performed ablution, offered prayers and left silently.
“Now, most of the visitors are from nearby villages and Bajoga town. You hardly see more than 10 people, even on Mondays and Fridays when many visitors used to come to the place,” Bello said.
He added that there was a well where people drew water to perform ablution before entering the grave site, but it has dried up and people now come with their water, either in small containers, or they purchase sachet water before coming.
“The lack of water is part of the reasons people are not coming as they did in the past. As you can see, this place is located in the middle of farmlands; the closest village is about 200 metres. And people believe they have to perform ablution before entering the place,” he further said.
There’s an abandoned structure adjacent the tomb site.
Bello said the project to construct a mosque and other small halls adjacent the tomb site was started by the authorities of Funakaye Local Government Area, but it was abandoned due to lack of funds.
Located about 50 metres north of the Sultan’s tomb is the chief imam’s grave, who was also killed during the battle. His tomb is equally abandoned, with fencing done halfway; and there’s no door at the entrance.
Also, the situation at the tomb of Major Marsh, located about 150 metres from the Sultan’s, is not different. The construction of a wall to fence the tomb was abandoned and the place is completely inaccessible as grasses have taken over. The grave is not even visible.
According to residents of Bajoga, in the past, relatives of the late Major Marsh used to visit the place occasionally to offer prayers, but for several years now, they have not visited.

Muhammad Yarima Lamu (Yariman Bajoga) was born in Bajoga town 78 years ago, some 40 years after the famous battle of Mbormi. The elder brother to the present district head of Bajoga said when they were growing up, people from far and near used to visit the place to offer prayers and seek blessings from Sultan Attahiru I, who many people, especially his Fulani kinsmen who were the major visitors to the tomb, consider as Saint.
Asked if the presence of the tomb near the town had brought any blessing to the people, he said, “It can’t be ascertained. Even if there is any benefit, it is not so pronounced to make any noticeable impact on the lives of our people.”
He added that there is no record that any reigning Sultan of Sokoto had ever visited the tomb; from his successor, Sultan Muhammad Attahiru II to the present Sultan Muhammad Sa’ad Abubakar III.
According to Lamu, in the past, some descendents of the late Sultan from Sokoto used to visit.
“In fact, even the wall fencing the tomb was built by the descendents of Sultan Attahiru I who were able to escape during the battle and migrated to settle in Sudan,” Lamu said.
Lamu further said Mbormi was founded by one Modibbo Jibrin Zai, also known as Malam Gaini. He was expelled from his birthplace in the present Katagum Emirate of Bauchi State. He settled in Gombe, where the fourth Emir of Gombe, Abdulkadir Zailani gave him a farm called Mbormi.
“Malam Jibril, therefore, proceeded to develop Mbormi into a stronghold and continued to attract even more followers. He erected walls around the place and dug two trenches, one inside and one outside the wall. He fought several battles with about four successive emirs of Gombe and succeeded in taking over many towns under their emirate.
“Sultan Attahiru arrived at Mbormi not long after the British forces defeated Modibbo Jibrilla in a battle and took him to Lokoja, where he died. Apparently, the Sultan decided to break his journey at the town after he heard of their hostility against the British,” he explained.
The battle of Mbormi in 1903
After the defeat of the forces of Sokoto Caliphate in March 1903 by the British, Sultan Attahiru I and his followers stopped over at Mbormi, probably on their way to Saudi Arabia.
Sarkin Musulmi Muhammad Attahiru Ahmad, better known as Sultan Attahiru I, emerged as ruler after the death of Sultan Abdurrahman in 1902. He died during what was known as the fiercest resistance against colonialists in northern Nigeria.
The battle took place in July 1903. The Sultan’s men fought against the British forces with spears, swords and poisoned arrows. Some rode on horses while the rest moved on foot, but they believed their cause was just.
It was learnt that the battle, which started in the early hours of July 29, 1903, under the command of Major Marsh, lasted until 6:45pm.
Major Marsh was hit in the thigh by a poisoned arrow at the beginning of the battle, and he died within 20 minutes.
Narrating how the Sultan was killed, Malam Lamu said, “After a hard battle, the British forces managed to enter the town. The Sultan was praying in the central mosque, but after he heard that they had broken the wall and entered into the town, he walked out and was subsequently shot in the forehead. He died by the wall of the mosque and was buried very close to the mosque.
After the battle, the then Emir of Gombe, Umaru Kwairanga and some of his men visited the scene of the massacre and made sure the Sultan was decently buried. Thereafter, British authorities destroyed the town and declared that no one should ever live there again; hence Mbormi is now desolate, and apart from the tomb, one can only see a vast farmland populated by numerous baobab trees.”

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.