At least 325 deaths have been recorded in the fresh outbreak of cholera in the country.
Six states reported 1,786 suspected cases of cholera between June 20 and June 26, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), said in Abuja on Saturday.
- Anambra 2021: YPP asks court to void APC, PDP governorship primaries
- INEC job: Evidence shows Onochie lied to Senate panel
NCDC’s Director-General, Dr Chikwe Ihekweazu, listed the states as Bauchi, 1,239 cases; Kano, 362 cases; Niger, 62 cases; Zamfara, 55 cases; Kaduna, 59 cases and Plateau, nine cases.
He told the News Agency of Nigeria (NAN) that in the preceding week of June 13 to June 19, five states: Bauchi, Kano, Kaduna, Plateau and Zamfara reported 1,757 suspected cases.
Bauchi State reported 900 cases, Kano State reported 575 cases, Kaduna State reported 70 cases, Plateau reported 98 cases, while Zamfara reported 114 cases.
Ihekweazu said between January 2021 and June 27, a total of 14, 343 suspected cases of cholera were reported from 15 states and the FCT.
The affected states are Benue, Delta, Zamfara, Gombe, Bayelsa, Kogi, Sokoto, Bauchi, Kano, Kaduna, Plateau, Kebbi, Cross-River, Nasarawa, Niger and the FCT.
NCDC’s Situation Report on cholera indicates that 27.6 per cent of victims across the country were those in the five years to 14 years bracket.
The report also indicates that 51 per cent of the suspected cases were male, while 49 per cent were female.
Ihekweazu also told NAN that a multi-sectorial National Emergency Operations Centre (EOC), coordinates the cholera national response activities.
“The EOC is co-led by the Federal Ministry of Environment and that of Water Resources given the link between cholera, water, sanitation and hygiene.
“The centre has been supporting states to ensure a coordinated, rapid and effective response to the current outbreak.
“This includes the deployment of National Rapid Response Teams to support the response at the state level, provision of medical and laboratory supplies, and scale-up of risk communications amongst other activities,’’ he explained.
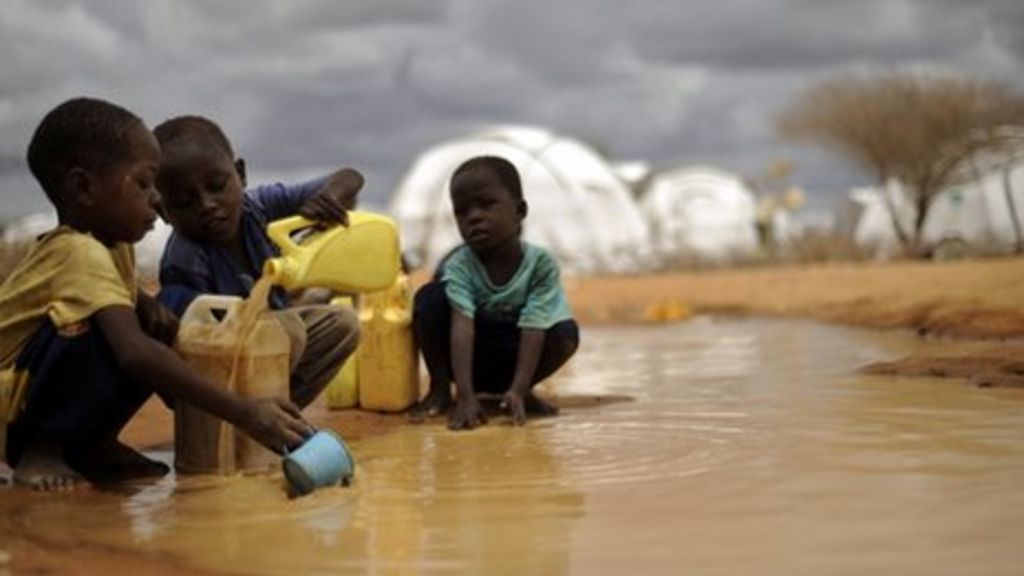
Cholera is a preventable and treatable epidemic-prone disease transmitted by eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
The incidence of cholera tends to increase during the rainy season. (NAN)

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.