By Risikat Ramoni
Mrs Moji Alakija and her child Dotun went to the sickle cell clinic at Gbagada General Hospital to complain about his frail health. Despite being a sickle cell patient, the dark-complexioned young boy continuously plays and climbs the stairs until he falls ill. The consultant attending to him, Dr Tunji Alakija, examined the child, prescribed drugs as well as a four-day injection for him, and then advice she takes him for a scan when he recovers.
Dotun’s mother is one of the many parents who take their children to the dedicated clinics organized by the sickle cell foundation Nigeria at the Gbagada General Hospital in Lagos.

- PODCAST: Finances In Marriage: Who Pays For What?
- Jos crisis: I won’t kill my father because of religion – Speaker
Patient’s experience
Samuel Yusuf, a 23-year-old 300-level student at the Lagos State University (LASU) had a leg ulcer in 2015. It started as an itch and he was told it was a leg ulcer but due to poor management, it expanded. He was later referred by someone to the foundation and he has been a regular visitor since 2020.
Some months after he commenced treatment there, it healed. But, after some time, it reoccurred and he has been managing the fresh ulcer since then.
The young man seems worried as he was informed that the older one gets, the longer it takes for the ulcer to heal.
“Dressing the wound constantly as well as taking medications makes the ulcer heal. But my challenge is, anytime I visit the foundation to manage my leg ulcer, I am unable to attend lectures. I miss classes for two weeks before returning to school. Most hospitals don’t know how to handle or manage leg ulcer effectively because they treat it like normal wound, only the foundation does it well. When the wound is not dressed when it should, the pain is excruciating and there is no amount of pain relief that will make it go away. It becomes difficult to sleep and there is nothing like concentration in class due to the overwhelming pain,” Samuel laments.
Another patient, Towobola Adigun, whose leg ulcer started in 2019 has a wide leg ulcer due to poor management at inception.
“The pain in my leg was too much. I could neither sleep nor eat for a month. People started running away from me due to my frail stature. A matron urged me to visit the foundation and, on that day, when my wound was cleaned and dressed there, I got home and slept like a newborn and I also ate well. Ever since, I have been a regular visitor there because I was surprised it was absolutely free.”
Towobola continues, “My challenge is with going for the dressing. I spend N1,000 from my house on the Island to the Foundation every time I visit. I have no husband to support and I have no job as nobody wants to employ me once they know I am a ‘sickler’.”
Burden of the disease
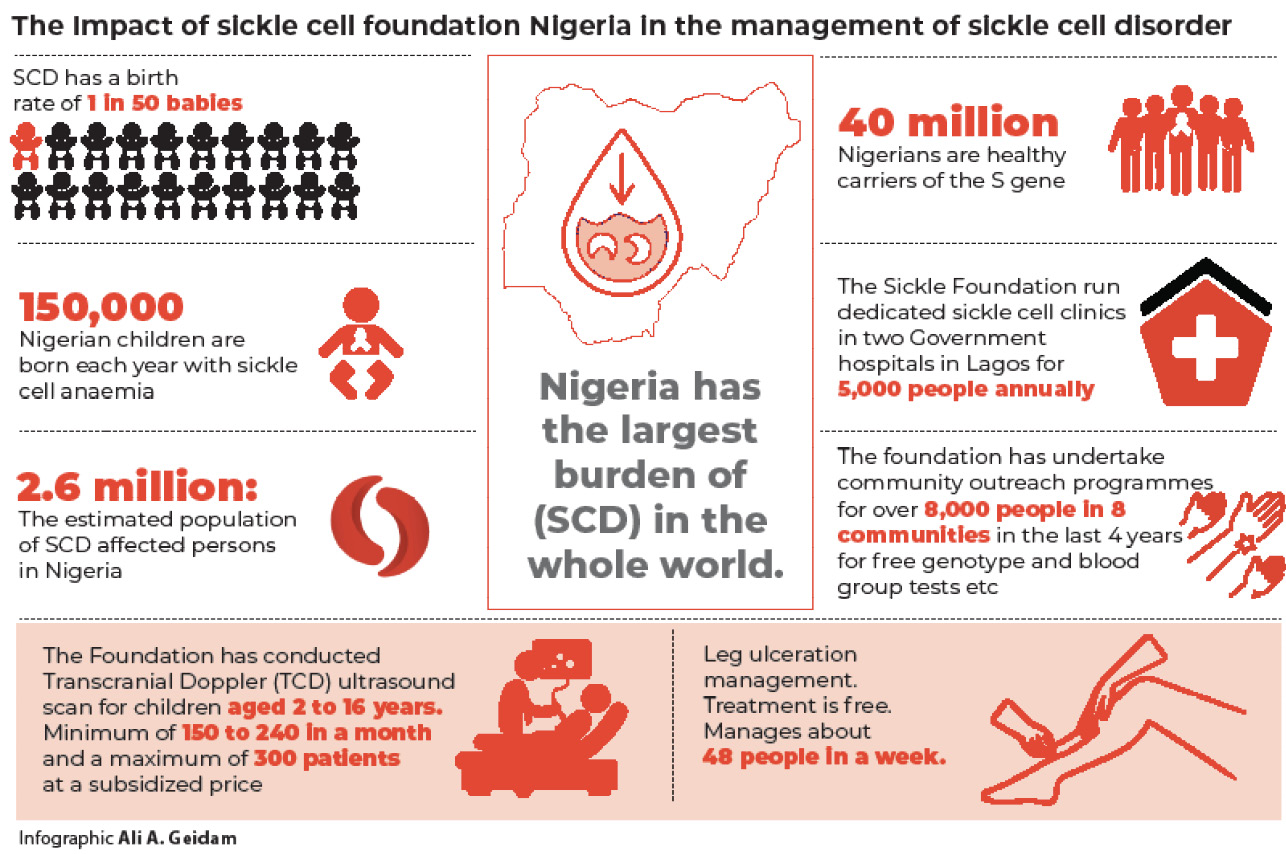
According to statistics from experts, Nigeria has the largest burden of sickle cell disorder (SCD) in the whole world. Prof Olu Akinyanju, a renowned expert in sickle cell management, says one in 50 babies in Nigeria is born with sickle cell disease. The estimated population of SCD affected persons in Nigeria is about 2.6 million, owing to a high rate of premature deaths.
Every year, 150,000 Nigerian children are born with sickle cell anaemia (HbSS), the prevailing type of SCD in this part of the world. Forty million Nigerians are healthy carriers of the S gene; they are either HbAS or HbSC.
Sickle cell disorder is a complex condition that requires care so the child born with it would not die prematurely before the age of five due to lack of access to early diagnosis and proper care. Some SC children have stroke, some have crises every now and then, which makes them visit the hospital on a regular basis while others have leg ulcers when they are in their teenage years.
Management of sickle cell
To effectively manage the condition, Prof. Akinyanju founded a national sickle cell center (now known as sickle cell foundation Nigeria) in 1994 to address a comprehensive care, management and control of SCD in Nigeria.

Over the past 10 years, doctors and nurses from the Foundation have been attending to patients at the Gbagada General Hospital every Thursday and they have also been regularly visiting Massey Children Hospital every Wednesday and Friday to consult as well as give drugs for free to sickle cell patients. Over the years, at least 5,000 people benefit from the dedicated sickle cell clinics annually. This has helped reduced the burden on indigent parents who could not afford high hospital bills to manage the expensive condition.
“At the dedicated clinics, we attend to only children in Gbagada since the adults are being attended to at the hematology section of the hospital while in Massey, we attend to children till they clock 18, then refer them,” a nurse, Mrs. Esther Shobamiwa relates.

“On every clinic day, we pray, give the patients and their parents 30 minutes health talk on sickle cell then take their vitals. We then separate those who have complaints from those who don’t. Those who have no complaints take their drugs and leave while those with complaints see the doctor, take their drugs and leave, all at no cost. After examining them, if need be, the doctor recommends and refers them to the Foundation for a comprehensive test, scan or management of their ailment.”
Despite the regular clinics every week, it was discovered that many people could still not be reached and many are lacking basic information about the disorder. So, a community outreach to the rural areas in Lagos such as Epe, Badagry, Ijede, Ibeju lekki, among others, were targeted by the Foundation. Through the community programme, over 8,000 people in eight communities in the last four years have been reached. At the outreaches, free genotype and blood group tests, health talk, free medical consultation and drugs as well as genetic counseling were done. The beneficiaries were given a genotype card which shows their genotype and blood group.

“We met an 80-year-old woman in one of the outreaches. She never knew her genotype. It was at the outreach she knew she was AS. She had eight births and only one child survived. Chances are that her husband too was AS and they had only one AS or AA child,” Mr. Ebenezer Adeleye, the Foundation’s programme coordinator told Daily Trust.
Specialized care
Sickle cell patients need specialized care which would ensure they stay healthy. One of such care is a regular ultrasound called TransCranial Doppler (TCD) scan. The TCD is a 15-minute painless scan important for all children living with sickle cell to prevent them from having stroke. Children between two to 16 years are prone to having stroke. Stroke in children can be serious as a part of the body may be paralyzed, mobility will be affected and sometimes the neurological system. There can also be a repeated stroke. So, to avoid it, the TCD is compulsory for all of them.
The HOD of TCD Dept at the Foundation, Abimbola Olukotun, emphasized that, “A child is expected to do the test only once a year. If the scan result comes out as low-risk or standard, the next appointment will be in one year’s time. If the result is conditional, it will be repeated in three months. If the result eventually turns to high-risk, it will be treated as an emergency.”

On the number of patients seen at the department, Olukotun said when schools are in session, there are usually 150 to 240 patients in a month, but during the holidays, there are up to 300 patients monthly.
TCD is an expensive scan which cost 350 pounds in the United Kingdom and over N78,000 in some private hospitals in Nigeria. At the Foundation, it cost N5,000 to conduct the scan.
“The TCD has been highly subsidized by the centre as the money collected is only for consumables. A TCD machine cost 15,000 pounds. The machine was donated in 2011 that was why we are able to subsidize it. Patients from General and private hospitals in Lagos and many parts of the country visit the centre for TCD,” says Mr Adeleye.

Another specialized care done at the Foundation is the chronic leg ulcer management. The leg ulcer, regarded as a stubborn wound, is more common in males than females and it starts when a child is above 12. At the Foundation, free treatment is provided for them till the ulcer heals. Every Monday, Wednesday and Friday, patients visit the facility to clean and dress the wound, then on Fridays, they take a free pack to clean by themselves over the weekend or find someone to do it for them. On the average, 48 people with leg ulcers are managed in a week.
“Although patients are usually enjoined to eat fruits and take drugs to make the wound heal faster but many of them cannot afford it. Some do not visit the center regularly due to financial incapability and this prolongs the healing. The Foundation gives them transport fare but that has stopped due to inadequate funding,” Nurse Kemi says.
Limitations
Adeleye relates, “Major limitation is funding. When the fund comes, we will be able to do more. When there was adequate funding, patients at the Gbagada and Massey clinics were given three months drugs for free. Now, due to lack of fund, they are given only one month drugs free and are asked to procure the remaining ones at the nearest pharmacy. The Foundation survives on donations. Treatment and care are usually for everybody but the main targets are the indigent.”

Adeleye further says, “More machines and consumables for the TCD are needed in every state of the country as it is a life-saving equipment. We need support to achieve this so people won’t have to come from other states for the TCD as they do at the moment. It should be in at least one government hospital in each state. It should be part of the routine test for every child who has sickle cell.”
“Lack of manpower is a major challenge. The foundation needs someone to go round the hospitals, especially government-owned ones where there are lots of people to educate them on sickle cell management. This still needs funding too,” Nurse Shobamiwa mentions.
Having a child with sickle cell disorder is not a death sentence, with adequate care and support, the child would survive and grow to become an adult.
This piece is with support from the Solutions Journalism Network and Nigeria Health Watch.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.


