It has been two weeks of devastation and sorrow as I lost a close friend of mine diagnosed with cancer of the Liver. Kindly use your weekly health column to educate us about the problem.
Kelechi V.
Thanks Kelechi for your question and may his or her soul rest in peace. Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of the liver. The liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of the abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and above the stomach.
The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.
Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung or breast and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer.
Symptoms
Most people don’t have signs and symptoms in the early stages of primary liver cancer.
- 1. Losing weight and Loss of appetite
- 2. Upper abdominal pain and Nausea and vomiting
- 3. General weakness and fatigue and abdominal swelling
- 4. Yellow discoloration of skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- 5. White, chalky stools
Causes
Liver cancer happens when liver cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA is the material that provides instructions for every chemical process in your body. One result is that cells may begin to grow out of control and eventually form a tumor, a mass of cancerous cells. Sometimes the cause of liver cancer is known, such as with chronic hepatitis infections. But sometimes liver cancer happens in people with no underlying diseases.
What are the risk factors?
- 1. Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- 2. Cirrhosis. This progressive and irreversible condition causes scar tissue to form in the liver.
- 3. Diabetes. People with this blood sugar disorder have a greater risk of liver cancer than those who don’t have diabetes.
- 4. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. An accumulation of fat in the liver increases the risk of liver cancer.
- 5. Exposure to aflatoxins, poisons produced by molds that grow on crops that are stored poorly. Crops, such as grains and nuts, can become contaminated with aflatoxins, which can end up in foods made of these products.
- 6. Excessive alcohol consumption.
How to prevent cancer of the liver?
- 1. Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all.
- 2. Maintain a healthy weight.
- 3. Get vaccinated against hepatitis B
- 4. Know the health status of any sexual partner.
- 5. Don’t use intravenous (IV) drugs, but if you do, use a clean needle.
- 6. Seek treatment for hepatitis B or C infection.
How to diagnose cancer of the liver?
- Blood tests.
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT and MRI.
- Liver biopsy. Removing a sample of liver tissue for testing.
What are the treatment options?
- Surgery to remove the tumor.
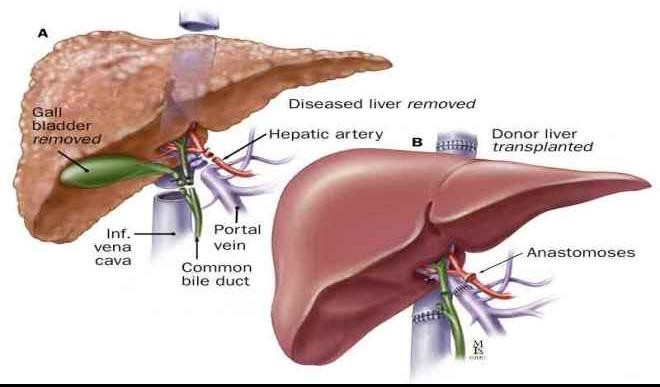
- Liver transplant surgery. During liver transplant surgery, a diseased liver is removed and replaced with a healthy liver from a donor. Liver transplant surgery is only an option for a small percentage of people with early-stage liver cancer.
- Radiofrequency ablation uses electric current to heat and destroy cancer cells.
- Cryoablation uses extreme cold to destroy cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy. This treatment uses high-powered energy from sources such as X-rays and protons to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.
- Immunotherapy uses one’s immune system to fight cancer.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill rapidly growing cells, including cancer cells.
- Supportive (palliative) care. Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.


