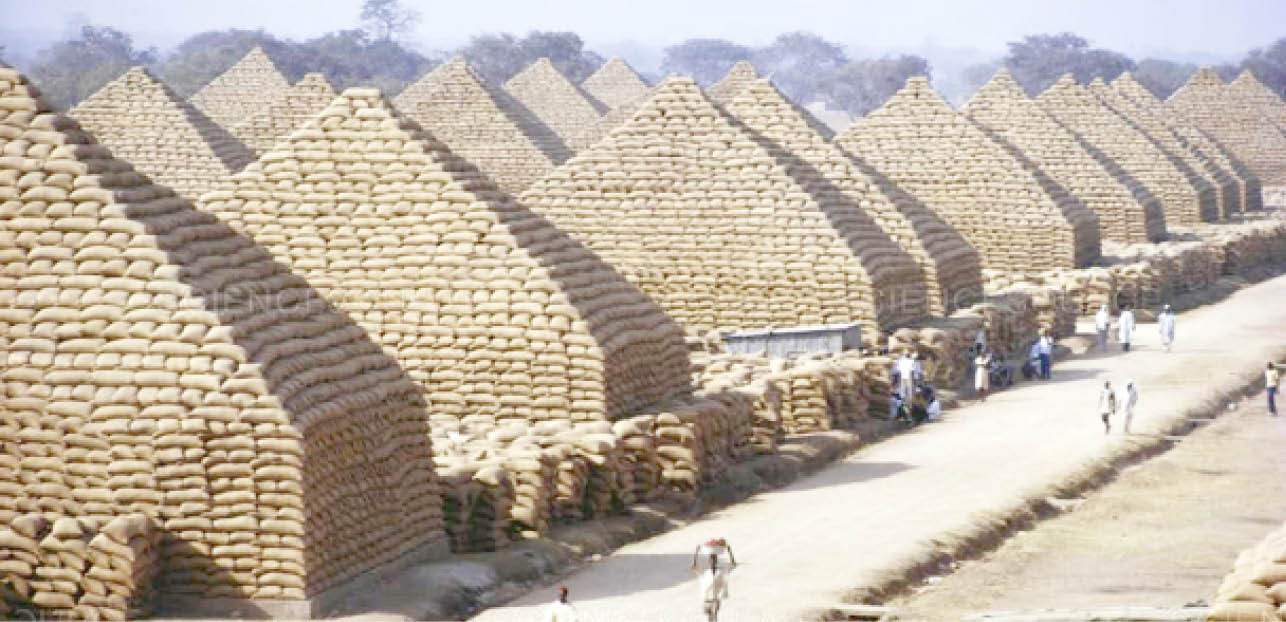
When a rice pyramid emerged in Abuja early in the year as part of activities to showcase the success of the Anchor Borrowers Programme, through which massive rice production was said to have been achieved in the country, it brought a nostalgic feeling among the older generation of Nigerians about the days when groundnut pyramids in Kano were part of the pride of the country. Over the years, the groundnut pyramids disappeared and buildings have now taken over their sites. Daily Trust on Sunday looks at the history of this aspect of Nigeria’s agricultural development and the possibility of returning the groundnut pyramids.
For several decades, Kano State has been home for agricultural produce. At a time, the state became synonymous with groundnut pyramids, which served as its symbol.
The pyramids were structures made from groundnut sacks. The nuts were said to have been grown in Kano and other places.
It is on record that in those years, groundnut production was a strong pillar in the economy of Nigeria’s First Republic, as well as key source of income to the colony and the colonial masters.

In those years, the pyramids were regarded as monuments and tourist attraction sites, as well as a symbol of northern Nigeria’s wealth. Up till today, Kano State prides itself as the city with the groundnut pyramids.
According to history, the pyramids were said to have been invented by a famous businessman in the region, Alhassan Dantata. He was one of the most successful businessmen supplying the Royal Niger Company (RNC) with groundnut and other agricultural commodities.
It was gathered that the pyramids were created as a form of storage methodology, where bags of groundnut were kept and stacked in bags in the shape of a pyramid before they were taken by train to Lagos and shipped out of the country.
Alhaji Haro Sule, a 76-year-old retired groundnut merchant, said that during that period, huge piles of sacks that rose higher than most of the buildings were a symbol of northern Nigeria’s abundance in agricultural commodities and other important cash crops.
“Alhaji Dantata was a very innovative businessman. It was observed that the pyramids were strategically placed at the centre of the production region and the head of the railway to Lagos.
“Kano was once a staging post in a thriving trade to the market in Europe. Groundnut was collected not only from Kano State but also from all other producing areas. Kano was serving as a central collection area and the pyramids were formed there,” Alhaji Haro said.
He further noted that based on sizes, an average groundnut pyramid could be made from as much as 15,000 full groundnut bags.
It was also gathered that the history of groundnut in Nigeria traces back to 1912 when most farmers were encouraged by high economic returns from groundnut; therefore, the marketing of the crop became well organised.
According to Ubale Usman, a grain merchant at Dawanau International Market in Kano State, at the end of each production season, agents moved to various parts of the region to purchase the produce while some farmers preferred to carry their produce by themselves to Kano city, where it was sold at a price fixed by an established marketing board.
But over the years, these pyramids gradually disappeared without explanation.
As the Kano pyramids collapsed and the field became open, buildings started emerging after some years, an indication that the monuments won’t return.
However, the Kano State chairman of the All Farmers Association of Nigeria (AFAN), Alhaji Abdulrasheed Magaji Rimin Gado, said that with the right policy and political will, the pyramids could be restored.
He said farmers had tried to see how the production of groundnut would improve, but the authorities did not help matters as they showed cold shoulders.
“For two years we have been pushing for the inclusion of groundnut in the ongoing Anchor Borrowers Programme, to no avail. It is apparent that the total groundnut production is dropping when compared to what obtained years back. Both farmers and traders have shifted to other agricultural produce.
“It is also clear that if groundnut has been given half of the attention rice is presently having, the pyramids would have returned. This decline in groundnut production has also affected industries that use it as raw material, to the extent that some of them have closed down or shifted to other oil seeds,” the AFAN chairman said.
He further revealed that various research institutes had come onboard, and they had done their best in the development of different groundnut seeds.
“The International Crops Research Institute for Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) and the Institute for Agricultural Research (IAR, Samaru) have joined the search for sustainable solutions to groundnut production in Nigeria. It will interest you to note that through collaborative research, extra-early varieties maturing in less than 90 days have been developed, with the ability to escape drought. Resistance to rosette has also been incorporated into these early maturing varieties. What groundnut farmers need is just a government with the political will,” he said.
But for Ibraheem Adam, a Kano-based businessman, the pyramids may not be revived because of the present multi-sector usage of the nut in Nigeria.
He said that without the present multi-sector usage, the pyramids would have probably been visible by now.
“If you make a simple analysis of the volume of groundnut being consumed by many companies across the country you would come to term with the fact that the pyramids may not be revived. But I am of the school of thought that had it been there were no such industries, the pyramids would have been present by now,” Adam added.

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.