What is roughly a distance of 10 kilometres on a dirt road with twists and turns could feel like a 50-kilometre road trip from the Musa Yar’adua Road in Kaduna’s Millennium city into one of Nigeria’s most successful private livestock ranches located at Kurmin Kaduna in Chikun Local Government Area. The trip to Zaidi farms, a 50-hectre farm land with improved cows, sheep and goats and a few birds is a testament to how crucial road accessibility and other amenities are to Nigeria’s agricultural sector.
As open grazing continues to pose disastrous challenges to both human and animal existence in the last 15 years; stakeholders within the livestock sector agree that ranching is presently the best option to limit farmer-herder clashes, improve animal health and also increase the country’s quality supply of dairy.
Experts say climate change is one of the biggest factors driving tensions between farmers and herders. As most parts of Nigeria’s Northern region continue to suffer desertification and drought, pastoralists who are mostly Fulani from the Northern region are forced to move deeper into the tropical savannah region in search of greener pasture.
At Zaidi farms, with over 250 cattle from the different breeds of Friesian, Simmental and Jersey, our correspondent reports that the ranch comes with a lot of modern facilities including pen houses, a milk parlour, mowers, tractors, hay barns and several others. Armed with decades of experience and a passion to revolutionise Nigeria’s livestock sector, Alhaji Idi Mukhtar, the Managing Director of Zaidi Farms, whose cattle are genetically inclined to give high dairy yield, said he was also working towards turning his cattle assets to Jersey breed. “They have the advantage of being of lower cost in terms of input; they are easier to handle, docile, malleable and they give as much milk as any other breed,” he said.
Standing proudly on his large expanse ranch with grasslands where he grows his own fodder to save him the trouble of the long drought season, Mukhtar said: “All you need is just one service bull and a local breed to start or you could use artificial insemination. Usually I advise people to start small.”
To raise livestock in an enclosed environment, pasture is a critical factor as the lack of it is considered the major reason why pastoralists travel far deeper into the lower belts for grazing. Mukhtar preempted this factor for his composition of 50 and 75 per cent cattle breeds and to mitigate challenges associated with fodder, he went into pasture development and is now self-sufficient in fodder. “My animals do not graze anywhere apart from my pasture land. I have a hay-ban with thousands of stacks. I have a buffer number because I went into pasture development ab initio,” he said.
In a harsh business environment that is further compounded by electricity challenges, diseases and insecurity, Mukhtar said a lot of peri-urban producers have been dissuaded from livestock while a lot of pastoralists have lost their animals. “We only do what we can and pray; we always live with that fear of insecurity and I have seen a lot of farms folding up and some people for fear of losing their stock sold off.
“You are dealing with Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia, foot and mouth disease, black quarter and others. If you manage the animals very well, some of these diseases can be kept at bay especially if you are dealing with liver fluke that comes from contaminated water. what I did was to sink my borehole; my animals don’t go to the stream to drink water,” he said.

Government must provide facilities for ranching – Herders
The dry season is the most challenging period for pastoralists and animals that walk long distances in search of pasture and water. Muhammad Hassan who has over 60 cows and grazes them openly said: “During the dry season, the rivers dry out and there is no green pasture for our animals. Sometimes we have to dig deep into the soil to find water for our animals.”
Hassan explained that he would love to ranch his cattle if only basic amenities were provided by the government. “The government provides markets, schools, fertilizer and seeds for farmers. If they give us water and fodder for the animals, we will not have to travel far,” he said.
His position was backed by Ardo Salisu Ibrahim Hari who owns 100 cows in Kauru Local Government Area of Kaduna State. Hari said even though their streams hardly dry up in Kachia, many herders resort to cutting down tree branches to feed animals from the leaves.
“Sometimes farmers burn down the grazing fields after their harvest to deny the cows food. Other times, youths hunting rodents will burn down the fields. Then there are other herders who migrate in search of fodder and they cut down trees which could bring problems for us if there were earlier agreements that such trees should not be cut down,” he said.
Hari who is also the Chairman of Miyetti Allah Cattle Breeders Association in Nigeria (MACBAN) in Kaura LGA said ranching was the best way as many herders were tired of cattle rustling in the forests and being killed in the cities. “It is not true that the Fulani do not want to ranch. We are tired of all the clashes and want to remain in one place where we can live comfortably and our animals can live freely,” he said.
Speaking with our correspondent, Rahinatu Mohammed, a milk maid from Romokosom in Kurmin Kaduna, said because of insufficient water and fodder, their cows are unable to produce sufficient milk, and urged the government to provide boreholes and grasslands in herder settlements. “We were told that the government was going to construct boreholes for us so we don’t have to move around with our animals, but we have not seen it. The animals now go to the stream and it is already drying out,” she said.
Idi Mukhtar however said ranching is not so simple, as Nigeria needs to get it right by providing basic amenities for the livestock sector to progress. “Electricity specifically is critical to the success of any ranch. No nation can make any significant economic progress without reliable and sufficient power supply especially in livestock development,” said Mukhtar whose cows’ daily consumption is about 100 litres of water per cow at the peak of the dry season.

With a borehole powered by solar energy to provide constant water for his animals, Mukhtar said this is because the national grid has become very expensive and unreliable. His milk parlour which presently milks six animals at a time with an ultimate capacity to milk 12 simultaneously is also powered by solar energy. The milk parlour has a 2,000-litre capacity cooling tank that has to remain at four degrees until the milk is evacuated. “You can’t run it on diesel; if you want to use solar you have to bring a lot of panels. You want to get hooked up with the national grid, but again, the question of reliability so ultimately, we’ll have to use solar for the milking tank,” he told Daily Trust.
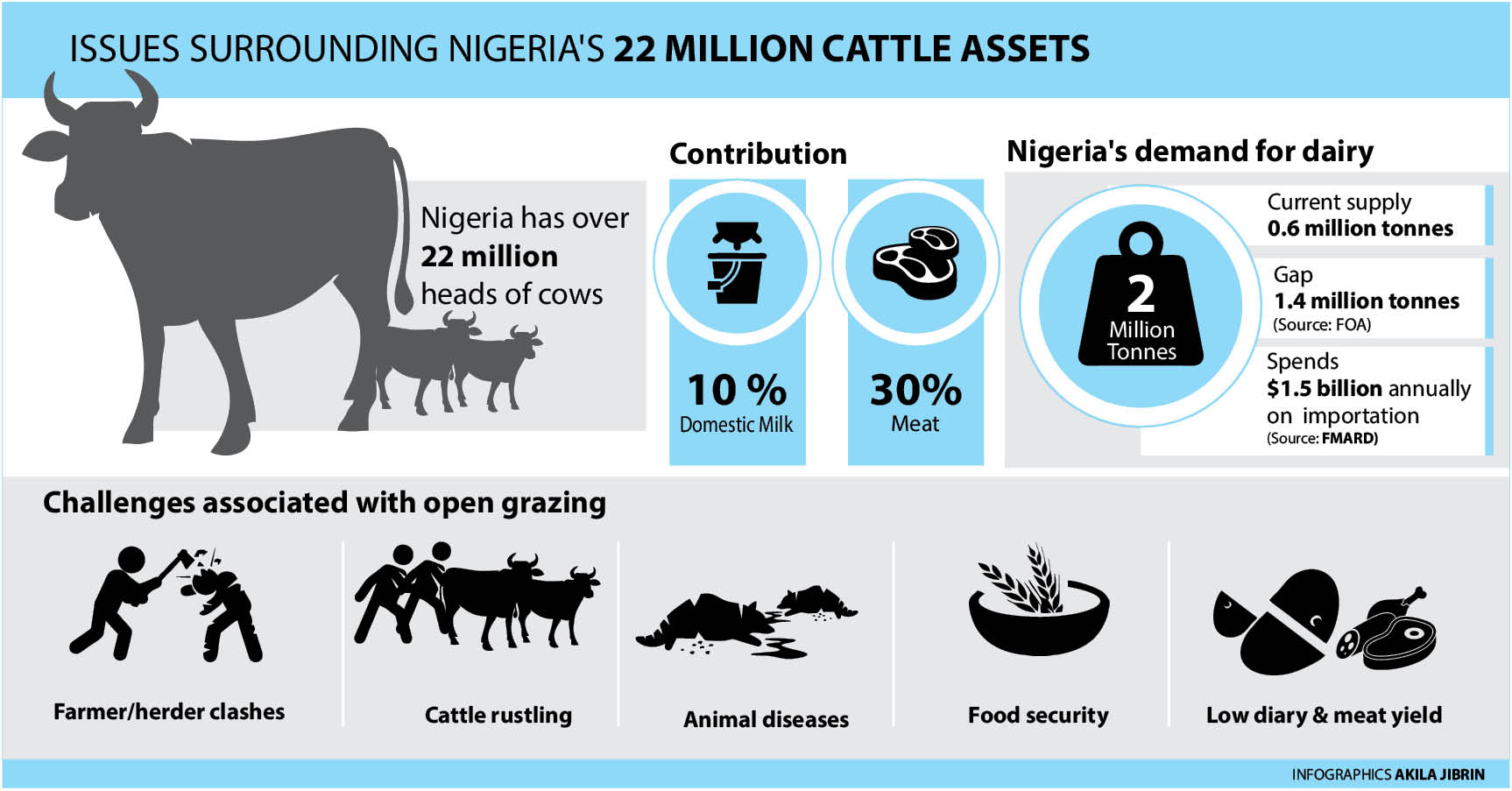
Nigeria has 22 million cows but less milk
Nigerian pastoralists do some milking every day but milk collection is done manually. Because of the dearth of chilling facilities, a large portion of the milk is consumed domestically. Through the Milk Value Chain Foundation, several collection centres have been created for milk maids to bring their milk for collection while they are paid at the end of each week.
At one of the collection centres within the Zaidi farms facility, Hadiza Jibrin and Halima Sadiya, both from Romukosom in Kurmin Kaduna combined, bring between a total of 35 litres daily and said the collection centre saves them the stress of having to trek to the nearest town to sell their milk.
“Now we have the guarantee that our milk will be bought and we will be paid at the end of the week,” Hadiza said. According to Sadiya, “I no longer have to hawk the milk, sometimes in the rain. Sometimes it degrades and we have to throw it away. Other times, people buy on credit and it takes a long time to get the money. We are grateful for this opportunity,” she said.
According to the Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations, Nigeria’s demand for dairy products is 2 million tonnes while actual supply is 0.6 million tonnes resulting in a gap of 1.4 million tonnes. The country’s Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development recently declared that Nigeria spends $5 billion to import food annually out of which $1.5 billion goes to the importation of milk and other dairy products.
There is no doubt that Nigeria’s 22 million cattle assets have not translated into sufficient dairy production with the FAO assessing the country’s contribution to only 10 per cent of domestic milk and 30 percent of domestic meat.
Even at a modern facility like Zaidi farms, the target is to produce 2,000 litres of milk daily but, at the moment, only produces 150 litres because the cows are milked once a day. “We need to complete a pen close to the parlour and irrigate the field then dedicate it to the milking cows so that as soon as they have been milked, they go to graze. They need eight hours grazing period and then we can start milking twice a day because grazing is about replenishing the body nutrients and energy that you extract from the milk,” he said.
Expressing frustration at Nigeria’s negligible milk production capacity, Idi Mukhtar of Zaidi farms said: “We have 22 million cattle yet we are not self-sufficient in milk production simply because our cattle are genetically limited. We failed to upgrade the genetic stock of the animals and that is why our yield is negligible.”
Executive Secretary, Agricultural Research Council (ARCN), Prof. Garba Sharubutu, believes that Nigeria can achieve dairy sufficiency if the National Livestock Transformation Programme (NLTP) is adopted and well implemented. “Nigeria has what it takes to get there but only if we practise the NLTP as wholesale but if we do it half way, then we can never achieve what we want in terms of milk and dairy sufficiency,” he said.
New livestock policies may improve yield
Idi Mukhtar of Zaidi farms believes that the neglect of the livestock sector is partly because the composition of the Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development is skewed against livestock. “About 80 percent of their activities is agronomic-based. What we are advocating for is the creation, either by presidential fiat or an act of parliament of the National Livestock Development Agency to focus on the livestock asset of this country,” he said.
However, Prof. Sharubutu believes that the structure of governance is not the problem but the implementation. “Before now we had the first Livestock Development Programme, we had the Fulani Amenity programme, and we had the second Livestock Development Programme. The problem is policy summersaults; when every minister comes, he comes with his own bias,” he said.
Sharubutu who is the immediate past Provost of the Federal College of Animal Health and Production Technology said: “We have established a National Veterinary Research Institute (NVRI) to fight disease; we have established a National Animal Production Research (NAPRI) for over 50 years. What have we come up with? Even if you are talking about neglect, you are talking about a trade with a high gestation period and so individuals have not been interested in going into it because it does not bring large and quick money like crop does.”
In order to create a vibrant livestock sector, the Nigerian government through the National Economic Council in 2019 inaugurated the NLTP in which the first phase of the implementation is geared to take place in Adamawa, Plateau, Nasarawa and Gombe states. It is estimated that job growth will rise to more than two million through the programme. However, the slow pace of the plan as well as resistance from certain regions of the country continues to pose a challenge.
Before the NLTP, the federal government had in 2016 entered into an agreement with Arla Global Products; a Milk processing company and makers of Dano milk, to empower local livestock breeders and promote a market-driven sustainable dairy development project in Nigeria. Known as the Milky Way partnership or the Milk Value Chain Foundation, the project comprises four groups led by Arla and three other partners including CARE in Denmark, the Confederation of Traditional Herders Organisation in Africa (CORET) and Danish Agricultural and Food Council (CEGES).
With the project currently taking place only in Kaduna State after a 2018 MoU with the state government, our correspondent gathered that the concept is expected to be replicated in other states across the country. “I am a beneficiary of that agreement,” said Mukhtar of Zaidi farms. “They visited some farms and saw what I was doing and they said I met the criteria. They supplied the milking parlour in my farm and the machineries including the cooling tank,” he said.
It is a similar situation at Amana Madachi in Igabi Local Government Area of Kaduna State where herders now have steady access to water and a milking parlour to ensure that the cows are hygienically milked and the milk is cooled down and preserved. The Project Manager, Milk Value Chain Foundation, Dr. Ishaq Bello, said an access road is ongoing at the foundation’s cluster at Amana Madachi.
Dr. Bello said with five major outputs, the project aims to increase the milk supply from the producers as well as their income, process and supply quality dairy product, expand the market as well as increase dialogue and collaboration within the value chain. Dr. Bello also said herders are trained in fodder feeds and feeding, herd’s health, managing the cooperative and how to keep records, access finance and manage diary business.
“We know that the traditional producer is interested in numbers not income because you could have 100 cows that give you 100 litres but you could have 10 cows that give you 120 litres. It is easier to manage 10 than to manage 100. So, we teach them those business concepts and financial literacy and most importantly, we also do milk and milk hygiene,” he said.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.


