Malam Sule Hamza, a 75-year-old resident of Gishiri Wuya village, sat in fear worrying over what to do if the predictions of another flood disaster this year should come to reality. He and other residents are yet to recover from last year’s flood which ravaged their village, destroyed houses, farmlands and also forced them out of the village to another location.
The aged man said he still has shivers from thoughts about how he suffered to get food for his family of four wives and 30 children. They ate rotten maize as a result of hunger, owing to the flood disaster, which he said destroyed over seven hectares of land that was expected to provide over 80 sacks of grains. The old man is yet to rebuild some parts of his house, so he used corn stalk to cover the dilapidated building his family still calls home.
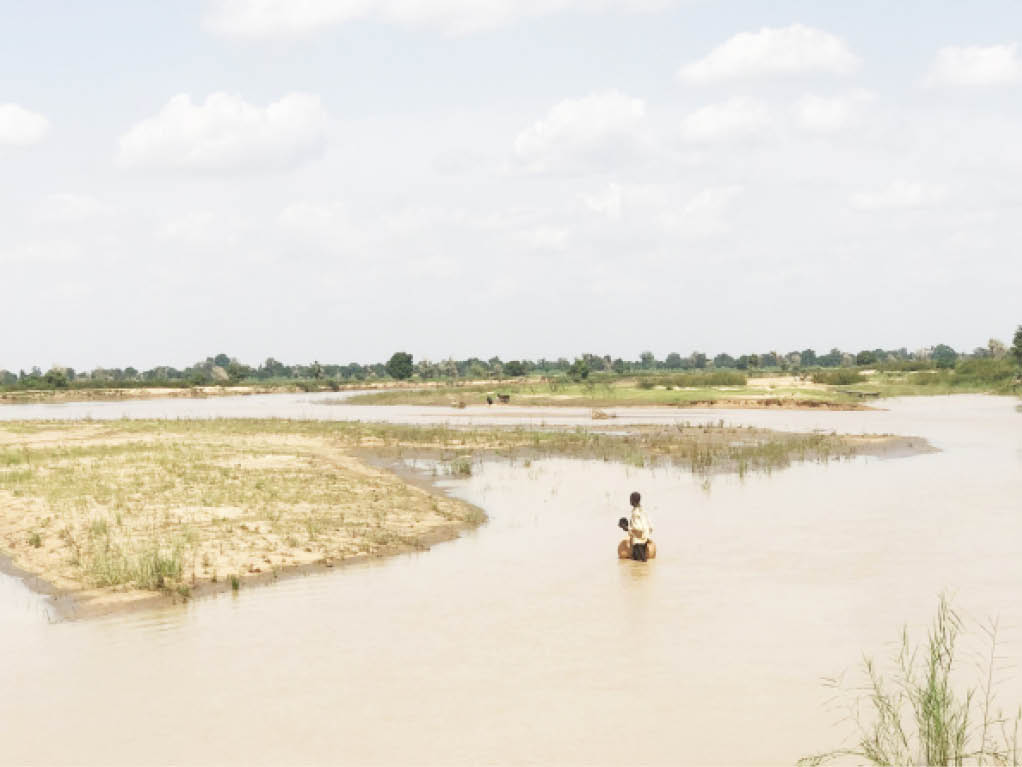
“Last year, I was left with nothing. We spent many days without sleep as the rain, after washing away our farms, was attempting to enter our houses. We were there in the bush every day and night packing sand inside sacks to prevent our village from getting flooded. After the rain persisted, we had to relocate to a school far away from here, where over 50 of us stayed in a single classroom,” he recalled.
Like Malam Hamza, residents of Gishiri Wuya and Katakarwa villages located in Larabar Gadon Sarki ward of Warawa Local Government Area were among the victims of the 2022 flooding which wreaked havoc on farmlands and displaced many of them. Their village is said to be the most flood-prone area in the whole surrounding as they sat in the middle, which made them vulnerable to the devastating flood that occurs every year.
- 2023 polls: INEC expresses worry over result management crisis
- Alleged N7.9bn fraud: Oduah, others arraigned, plead not guilty
The National Ad-hoc Committee on Flooding disclosed that 104,000 houses were destroyed while 172,000 persons were displaced by the flood in 2022 while 201 persons died and 108 were injured by the flood across 16 states of the country.
Similarly, the National Emergency Management Agency (NEMA) revealed that in the year 2022, Kano recorded 23 deaths by flood which also destroyed 14, 496 farmlands across 16 LGAs that were affected in the state.
Gishiri Wuya of Warawa LGA lost 2,248 farmlands comprising hundreds of hectares. The remote village, which comprises of over 500 households, with no school and clinic, is yet to recover from last year’s flood, amidst the prediction of another disaster by the relevant stakeholders in the environment sector.
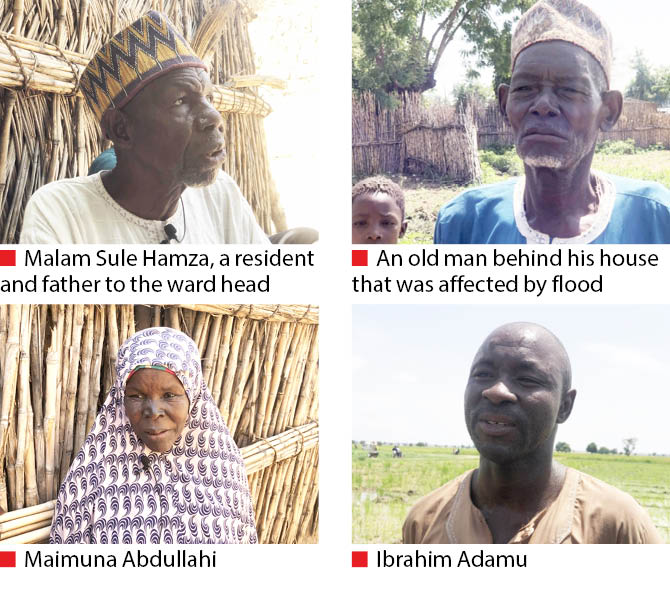

Recounting his ordeal further, Malam Hamza, who is a father to the village head, said their village is like a trap as they have no way to escape unlike other villages, adding that every year, they are after protecting their lives not their farm produce since they cannot control the flood.
“Gishiri Wuya is always the most affected and most flood-prone village in this area. We are surrounded by the water and when the flood comes, it puts us in the middle to the extent that we cannot escape. I wish you came here a few weeks ago when we were eating rotten maize. The situation is forcing us into serious hunger. As you can see, we are yet to rebuild our houses and yet they said another flood is coming.
“For the farm inputs, we don’t have hope at all. For almost three years now, the same thing has been happening. We will invest in our farms, and spend money along with hard labour, but towards harvest time, floods will wash everything away. Last year, I lost everything. I was expecting at least 70 sacks of rice, maize and millet,” he lamented.
For Mubarak Ibrahim, a father of four, the flood has been the most dangerous disaster he has ever witnessed in his life. For him, his dreams of becoming a big farmer have been dented by the reoccurrence of floods in the area where his only farm is located.
“The youths in this region largely depend on farming to get not only food, but a means to good life, but our hopes are threatened by the occurrence of floods every year. Many of us lost our little capital and now only work as labourers on farms.
“We don’t know what to do. Many of us have resorted to dry-season farming. But it is costly at this time of fuel subsidy removal. Not all of us can afford to buy fuel. We have to work for others for some token. Before I used to harvest 500 sacks of rice,” he said.
One year after disaster, nothing done to prevent future occurrences
According to him, following another warning of flood disaster this year, the residents have no option but to watch and do the little they can to reduce the dangers. “Nobody came here to support us with a penny, neither do they come to provide anything that will prevent another flood disaster.
“We relocated ourselves during the last flood and we came back by ourselves. We are left alone to provide a solution for ourselves, although all our wealth was submerged by the flood,” Ibrahim said.
Daily Trust Saturday reports that the Nigerian Meteorological Agency (NiMet), Nigeria Hydrological Services Agency (NIHSA), and NEMA in their various predictions, have identified Kano and 31 other states of the federation and the FCT as states that fall within the highly probable flood risks areas for 2023.
The report stated that floods in highly probable flood-risk states are expected to be high in terms of impact on the population, agriculture, livelihood, livestock, infrastructure and the environment between April and November. According to the report, Nigeria has traditionally focused on post-disaster flood response rather than risk control that can lessen the impacts of the disaster.
However, despite these warnings, early signals and calls for preventive measures by various stakeholders, residents of the villages in the southern part of the state said nothing has been done yet to cushion the effects of the past 2022 flood disaster.
Ibrahim Adamu, a resident of Larabar Gadon Sarki, the neighbouring village to Gishiri Wuya, said the lack of structure that will demarcate them from the water is a threat that always exposes them to the dangers of flood.
He said every year they have to carry out make-shift embankment but they can’t do that this time around as it also required money.
“Our only hope every year is the embankment we usually do by filling sacks with sand. But last year, the flood crossed the embankment. After spending over 10 days in the bush, we had to relocate. At that time, we were not after our farmlands or houses. Our only concern was our lives,” he said.
Why we refused to relocate from village
Meanwhile, despite the plea by NEMA for residents of flood-prone communities to relocate to higher ground before the start of the flood season, some communities in the region, particularly those near the Wudil River, which is linked to the Hadejia Jama’are Dam in Jigawa state, have disregarded the advice which, according to them, is due to lack of alternatives.
During the past administration of Dr. Rabiu Musa Kwankwaso, a housing unit was said to have been built for the Gishiri Wuya residents to relocate to Danbare, a village close to their town. However, the residents rejected the houses on the grounds that the houses could not cater for all the members of the village.
“Yes, it is true that a housing unit was built. But during the distribution of the houses, it was not captured in a way we can leave our house. You know how households are in villages, in one house you will get five to eight people, each living with his family.
“What they did then was, for each of the houses, they gave one or two new houses. Like in our house, they gave us two. And we have seven households. There are some households with even two wives. The new house has only two rooms, how can we live in that kind of house? And they were going to demolish our own houses, so that was why we refused. Majority of us would have ended up homeless,” a representative of the ward head, Mallam Hamza said.
Embankment, good road and river dredging needed
Proffering solutions to the problem, residents of the villages said if they can get a new place that will accommodate their entire families, they would leave the place that did nothing but threaten their lives every year. However, they said the best way is to build an embankment that prevents the water and also repair their only linking road.
A widow and mother of seven, Maimuna Abdullahi, 62, said she lives with four of her children who are married to two wives each, and that they are passing through a lot relocating from the village every year, adding that the best solution is for the government and other stakeholders to help and repair the road and do an embankment that will surround the town.
“If I’m opportune to meet the state governor or any other person in charge of this, I will beg him to help us repair our road. The rain has started and we are living in fear every day. Last year, my daughter-in-law gave birth in the middle of a farm during the period.
“We don’t want to relocate from this place. This is where we live, we are used to the place and we have vast land for farming. The best way is to provide a solution that will address the problem,” she added.
Warawa among top gov’t interventions beneficiaries – NEMA, SEMA reacts
However, NEMA Territorial Coordinator for Kano and Jigawa states, Dr. Nura Abdullahi, said their agency in collaboration with the State Emergency Management Agency (SEMA) distributed relief materials to victims of the flood and the entire Warawa LGA is among the top beneficiaries.
“We went severally to the local government area and we distributed relief material. We shared foodstuff, building materials and even some items to help women engage in businesses.”
Dr. Abdullahi said the best method to prevent flood is by taking proactive measures and that “Those people in flood-prone areas have been given cautionary advice that they should relocate to other places. But unfortunately, before you know it, they will come back after the rain stops.”
Similarly, the Executive Secretary of SEMA in Kano, Isyaku Abdullahi Kubarachi, said they have embarked on public sensitization where they advised residents in those villages that are prone to flood to relocate before the disaster occurs.
He advised residents in the areas to relocate to other places, assuring that “Since the coming of our administration, we are working tirelessly towards addressing these disasters. We are coming up with a system that will focus on proactive measures against these disasters.”

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.