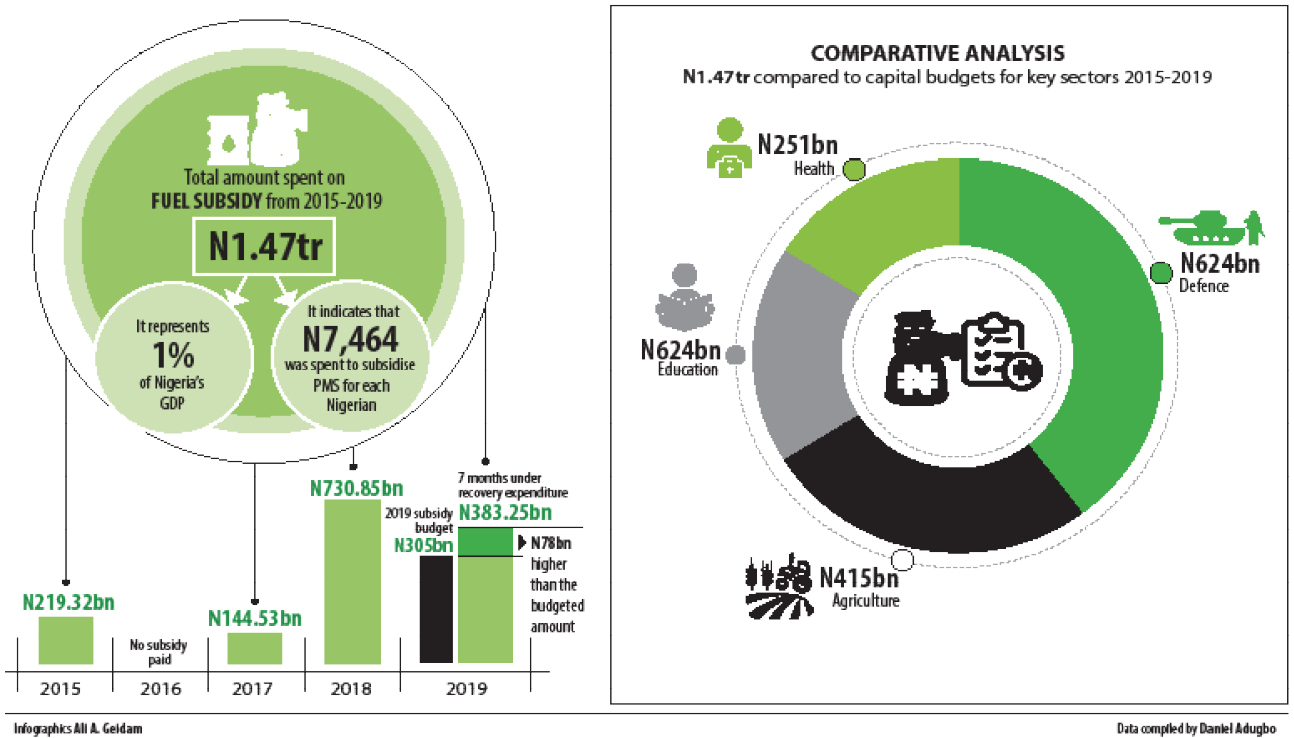
- Surpasses health, education, agric budgets
- Overshoots by N78bn in 2019
The current administration spent N1.477 trillion ($4bn dollars) on subsidy on Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) also known as petrol between May 2015 when the government was inaugurated and July 2019, Daily Trust reports.
The government has earmarked another N450 billion as fuel subsidy in 2020, but estimates based on current indices show that subsidy on petrol may hit about N5tr by 2023, when President Muhammadu Buhari ends his eight-year tenure.
Computations by this paper from official subsidy payments and deductions for under-recovery published by the NNPC between May 2015 and July 2019 show that the sum of N219bn was sunk into subsidizing petrol between May and December 2015.
Although no money was expended as subsidy on PMS in 2016, the government introduced another form of subsidy in 2017 which it described as “under-recovery.”
The subsidy incurred by the NNPC as under-recovery that year was N145bn and the amount rose to N731bn in 2018, representing about 405 per cent increase.
The total sum for subsidy from May 2015 to July 2019 stands at N1.5 trillion, according to the NNPC data.
A further breakdown shows that the amount spent as subsidy on PMS in the last four years represents about one per cent of Nigeria’s gross domestic product (GDP) of $397.30 billion (as of 2018).
It also indicates that between May 2015 and July this year, N7,464 was spent to subsidize PMS for each Nigerian, going by the National Population Commission (NPC) 2018 estimates of 198 million Nigerians.
FG overshoots 2019 fuel subsidy budget by N78bn
Data analysis carried out by Daily Trust showed that the Federal Government through the Nigeria National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) spent N383.2bn on fuel subsidy in the first seven months of 2019 alone.
The amount is N78bn higher than the N305billion budgeted for subsidy in the whole of 2019.
President Buhari had in December 2018, during his budget presentation to a joint session of the National Assembly said N305 billion (equivalent to one billion US dollars) had been earmarked for petrol subsidy in the 2019 budget.
However, data gathered by Daily Trust from NNPC’s monthly financial and operations reports showed that as at July 2019, the NNPC had exhausted the N305bn subsidy budget on PMS.
Although, President Buhari signed the 2019 budget in May, signalling the commencement of the budget cycle, existing indices show that subsidy on PMS would overshoot the N305bn target by the end of the life of the budget. Subsidy on PMS alone gulped N731bn in 2018, according to the NNPC data.
It is not clear from what sources the NNPC is drawing funds to offset the current subsidy on PMS. The corporation had in the past been accused of spending without appropriation by the National Assembly, while lawmakers say spending on fuel subsidy or related spending without their approval is extra-budgetary and illegal.
In 2018, NNPC said it initiated the move to raise a revolving fund of $1.05billion, since the corporation was, and still is, the sole importer and supplier of white products in the country.
The money dubbed the National Fuel Support Fund had been jointly managed by the NNPC, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), the Federal Ministry of Finance, the Petroleum Products Pricing Regulatory Agency (PPPRA), and Office of the Accountant General of the Federation (OGF), the Department of Petroleum Resources (DPR) and the Petroleum Equalization Fund (PEF).
The Buhari administration had in 2016, withdrawn subsidy on petrol, forcing independent oil marketers to pull out of importation of the product.
Their withdrawal left the NNPC as the sole importer of petrol. The pump price of PMS was fixed at N145 per litre against a landing cost of N180/190litre.
Since then, the NNPC has been drawing internal funds to cover the under-recoveries amounting to over N40/litre on the importation of petrol.
Fuel subsidy more than health, education and agric budgets in 4 years
A comparative analysis of the NNPC data on subsidy and the Federal Government budget from 2015 to 2019 showed that while the administration has sunk N1.5tr into fuel subsidy, the sum of N624bn has been committed to capital spending for defence, N415bn for agriculture, N277bn for capital components of education and N251bn as the capital budget for health in four years.
This implies that the cost incurred to subsidise petrol is more than budgets for capital projects for health, education, and agric (N943bn) sectors put together in the last four years.
The amount spent on subsidy is also larger than the N624bn; the capital component of the budgets for defence (including the army, navy, air force and defence intelligence as well as research agencies) in the last four years, though all the capital allocations traditionally, never get completely released.
By implication, less money went into building classrooms, hospitals and buying farm tools whereas more funds went into the petrol subsidy that experts have severally described “as economic waste amid scarce resources.”
The expenditure on subsidy for PMS has also dwarfed the government’s spending to alleviate poverty and youth unemployment.
Among promises President Buhari made upon which he rode to power were: investments in cutting edge health technology, a modernized agric sector, an adequately equipped military force and increased funding for the education sector.
However, available data showed that between 2016 and 2018, only N470.825bn was released out of the N1.5trillion budgeted for the government’s flagship poverty alleviation initiative, the Social Investment Programme (SIP).
The Buhari administration introduced the SIP made up of the N-Power, Conditional Cash Transfers, National Home-Grown School Feeding and Government Enterprise and Empowerment Programmes, GEEP) in 2016. From 2016 to date, the Federal Government budgets an annual sum of N500 billion for social investment. However, while only N79.98 billion was released in 2016, N140 billion was released in 2017 and N250.4 billion in 2018.
Experts comment
A consultant in natural resource management, Mr. Kolawole Banwo, noted that despite the huge amount of money spent on subsidy, it will be difficult for the government to muster the political will to do away with fuel subsidy.
He said, “first, due to a lot of policy decisions, there are rising cost of several things that have impacted on the citizens: electricity tariffs have gone up over time, the prices of food items have gone up generally and with the closure of the border there are indications that inflation rate has gone up. With the proposed increase in VAT from 5 to 7.5 per cent the chances are that prices of more things will still go up and that will further impoverish citizens.”
Banwo added, therefore, that subsidy removal in addition to the existing and imminent taxes, charges and levies, will not go down well with Nigerians.
“There are other issues about taxes, levies, PoS charges and all of these things will take money out of the pocket of the ordinary Nigerian. So, when you put all of these together, you will see that the removal of subsidy is going to worsen what appears to be a challenging rise in prices of general goods. Many things are happening at a time that will end up impoverishing Nigerians the more and for that reason, a government that promised change and wants to show Nigerians that it means well despite the challenges in the first four years, will not want to do such,” he said.
Leading energy lawyer, Dr. Adeoye Adefulu, said he does not think that the current government has the will to deal with the subsidy issue.
“The opportunities to do so have been available since 2015. The only move that the government made towards subsidy removal was in 2016, when it did price modulation but since then it has not shown any interest,” said Dr. Adeoye, who heads the Odujinrin & Adefulu’s Energy Practice & Real Estate and Mining Teams.
But an oil and gas expert, Abiola Rasaq, said the current government has the will and ability to push through a pseudo-market reform that will either directly or indirectly remove subsidy on fuel
‘‘That being said, it is important to understand the concerns of the government, which in my view are very genuine but perhaps overrated.
“First, fuel price increase has notable multiplier effect through transportation cost, given that mobility of goods and people is still largely through land transportation, with fuel-based vehicles
More so, the government is concerned about what the impact of any volatility in exchange rate may be on fuel prices if deregulated, as FX rate has notable implication for the landing cost of fuel.
‘‘Again, the government may want to get a better handle on true consumption of Nigerians. With the land borders closed and filling stations near borders closed, the purported consumption data should begin to normalise to reflect actual consumption of Nigerians,” he said. Rasaq said a way out of the fiscal concern is to subsidize other consumptions in the form of investment in public goods like; health, road, sewage and other infrastructures.
Speaking further, the expert said, “so, let’s look at it from this perspective, less than 1% of Nigerians have private vehicles and in fact some have 2, 3, 4 and perhaps some have dozens. In a regulated market for fuel, these are the people that get the most of the subsidy and the poor masses, who represent 99% of the population, who really need subsidy as a social support only, if at all, benefit from the subsidy indirectly through purportedly lower fares on public/commercial transportation of goods and people.
“If that is the case, we can think of creating a perhaps more effective subsidy by fixing road infrastructure and perhaps even at the extreme, invest or better still guarantee investment in public transportation like the BRT model.
“Again, we can channel the fuel subsidy into quality health care services either in the form of subsidised health insurance schemes with private sector HMOs or at the extreme, direct investment in primary health care, general hospitals and specialised healthcare. This will ensure that the poor masses get access to quality healthcare.
“Again, the poor masses also need quality education like the children of the rich. So, we can invest the subsidy in quality education for the poor. In many countries, public schools are as good as private schools. That’s direct and perhaps an effective way to alleviate the probable cost implication of deregulation. So, even if the poor masses, who need subsidy have to pay slightly higher fares for transportation and perhaps even pay slightly higher prices for food and other consumer goods just because of higher fuel prices, they can make up for the higher cost of these consumptions through savings on the social goods provided by the government. Perhaps, the poor would even be better off and such approach may perhaps help to more efficiently achieve the income redistribution and safety net that I think the government seeks to achieve”.
Another oil and gas consultant, Mr. Michael Awodeyin, said although the decision to remove subsidy is wildly unpopular, it is necessary because of its huge cost to the country.
“From the last time I looked at those figures, we are burning between N2bn and N3bn every day (on fuel subsidy). Assuming it is N2bn per day, it means that we are burning well over N1 trillion annually; that is a lot of money. Imagine if you take N1bn to build a hospital, it means that you can build a hospital in all the 774 local governments in Nigeria. Think about how many hospitals N1tr can build in a year.
“People would say prices of goods will go up if the government removes subsidy, already how many places do you have PMS at N145/litre? Go to the creeks how much are they selling PMS, go to the far North, the east and rural areas, it is almost N200 per litre,” he said.
Awodeyin said subsidy removal was the only way to curtail smuggling of PMS.
When contacted for his comments, acting spokesman for the NNPC, Mr. Samson Makoji, said he would revert with more information on how NNPC manages to sustain under-recovery on PMS. He was yet to respond as at press time. Also, spokesman for the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) Mr. Issac Okoroafor and the Director of Press in the Ministry of Finance, Hassan Dodo, did not pick calls or reply text messages sent to them on the matter.
 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.


