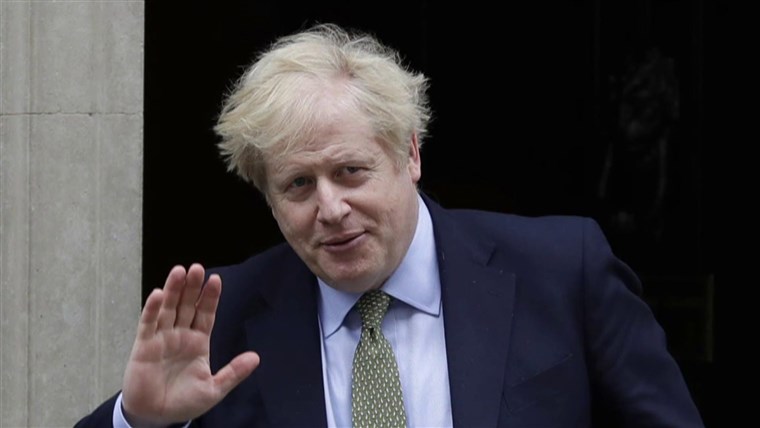
UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced Monday all pandemic legal curbs in England would end later this week, urging a shift from government intervention to personal responsibility.
But he faced scientific unease and claims of political calculation to shut down discontent at the restrictions and his premiership within his ruling Conservative party.
- FIFA World Cup Play-off: CAF announces new dates for Nigeria, Ghana battle
- Nigeria set to use atomic materials for energy supply – FG
Johnson, who has been mired in scandals that have threatened his hold on power, said the legal need for people to self-isolate when infected with COVID-19 would stop from Thursday.
Access to free home testing kits will also cease from April 1, he added.
“We now have sufficient levels of immunity to complete the transition from protecting people with government interventions to relying on vaccines and treatments as our first line of defence,” he told parliament, to cheers from the Tory ranks.
Johnson pushed ahead with the changes despite news that Queen Elizabeth II had tested positive for the first time, calling it “a reminder that this virus has not gone away”.
The 95-year-old monarch was experiencing “mild cold-like symptoms” but expects to be at her desk carrying out “light duties” this week, Buckingham Palace has said.
Opposition parties accuse Johnson of seeking to distract public attention, with his position in peril as police probe lockdown-breaching parties in Downing Street.
Keir Starmer, leader of the main Labour opposition, said the new measures were “not enough to prepare us for the new variants which may yet develop” and urged Johnson to publish the scientific advice underpinning his decision.
“We have to take the public with us and that requires clarity about why decisions are being made,” he added.
Under the plan, as well as ending the legal self-isolation requirement, the government will scrap all contact tracing of positive cases later this week.
It wants local authorities to manage further outbreaks with pre-existing legal powers and the private sector to provide everyday tests, while health agencies maintain stockpiles for possible future use.
Nationwide surveillance testing, in particular a respected weekly study run by the Office for National Statistics (ONS), will also be maintained to detect new variants.
The Confederation of British Industry’s Chief Policy Director Matthew Fell welcomed the government announcements as “a significant step towards normality returning” but called for continued state support for mass testing.
“Mass lateral flow testing has kept our economy open and firms continue to believe the economic benefits far outweigh the costs,” Fell said.
The British Chambers of Commerce echoed the concern, with co-executive director Claire Walker saying that the government “must not pass public health decisions on to the business community, who are not public health experts”.
But ahead of the announcement Robert West, a health psychologist at University College London and member of one of the government’s independent scientific advisory groups, said the changes were “irresponsible”.
“In lifting all these protections, there will be an increase in cases. And there will be an increase in hospitalisations and deaths,” he told Times Radio.
The NHS Confederation, which represents senior managers in the state-run National Health Service, said internal polling indicated a large majority of its members were opposed to ending self-isolation and free tests.
And David Nabarro, a World Health Organization special envoy for Covid, said scrapping the law on self-isolation was “really very unwise indeed” and Britain was “taking a line that is against the public health consensus”. (AFP)

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.