Millions of Nigerians live in slums in many state capitals without basic necessities of life despite their closeness to the seat of power.
Findings by Daily Trust revealed that slums are sandwiched in metropolitan areas where people live in squalor and dehumanising conditions due to lack of basic necessities, a development that casts doubts on the role of government (s).
- 2023 Igbo President: A just cause for national devlpt
- Dan Amanar Daura: Amaechi, the trusted son of Daura
Dwellers of such places are not only lamenting their poor living conditions but also calling for attention as their children have no access to good schools or recreation centres.
Most of the places visited by our reporters are densely populated and lacking infrastructure. They are characterised by poor sanitation and poverty indices.
The dwellers always have different stories to tell about their bitter experiences, especially due to the failure to access basic infrastructure that would have made life good for them.
Most of those who spoke admitted that raising children in such places was worrisome as they are prone to imbibing negative impressions about life.
Lagos
Findings by our correspondent show that Ajegunle is one of many chaotic slums of Lagos, where people from all tribes in Nigeria live.
The meaning of Ajegunle in Yoruba is, “This is where I have found my wealth.” But ironically, poverty is the second name of the busy slum called Ajegunle.
A 10-year-old Tayo and JSS 1 student of Temidire Secondary School in the Tolu area of the ancient ghetto, fondly called AJ City or Jungle City, had just returned from school on this fateful day.
He and many other children from poor homes had to trek several miles under the scorching sun to their different houses.
Like many other kids in Ajegunle, Tayo resides with his parents and seven siblings in a single room in a compound that houses 12 rooms, excluding the boys’ quarters located at the back of the main compound.
In local parlance, such abode is commonly referred to as “Face me, I face you.”
The boys’ quarters’ section has four smaller rooms that are wide enough to be used as stores. Each of the rooms has about 10 occupants who use one small space as kitchen. There is only one toilet and a bathroom which the about 100 persons in the compound use.
Tayo said that only his parents had the privilege of sleeping in the only 6×4 wooden bed in the room. To create a space where he and his siblings can sleep, the only chair and table in the room have to be removed, while the bed space is carved out with a curtain for privacy.
On a daily basis, tenants jostle to use the only toilet and bathroom in the compound. Some of them wake up as early as 4am to be able to beat their neighbours to the scramble for the facilities.

Owing to the pressure on them, stench that oozes out always fills the air.
Sunday George, a house agent who resides along Olowojeunjeje told our correspondent who visited the area that life in such environment was frustrating.
He added that people find it very difficult to survive in the place as their conditions continue to worsen.
“Every day, poor people from different parts of the country troop to Ajegunle in search of opportunities that are not easy to come by. There is extortion at every point. Only one in every 20 persons has a regular job,” George said.
He explained that Ajegunle has four major communities – Olodi, Tolu, Aiyetoro and Awodiora.
He also disclosed that a lot of people who reside at Tolu were mainly smugglers because of the proximity of the area to the seaports, while those who live in Olodi would prefer to be associated with Apapa.
“Aiyetoro is occupied mainly by the owners of the land, who are the Ojoras, while Awodiora is occupied by people with regular white collar jobs,” he said.
While narrating the poverty-stricken life of the inhabitants of the slum, Wale Ojo, the head of tricycle riders association at Ojo Road Park, said, “Cooking is not a problem for inhabitants. If you find out that you don’t have salt or pepper while cooking, you can ask your neighbour’s wife for it. Some bachelors can even wait for their neighbour’s wives to finish cooking before begging for soup without meat in order to eat their already made eba or fufu.”
A visit by our correspondent also indicated that two major popular streets in Ajegunle are Gorilla, also known as “Good Evening Street” and Bata, Off Nosamu, also known as “Excuse Me Bros, Chance Dey?”
Many residents of the streets are mainly old sex workers; and activities around the streets climax from 8.00pm till dawn.
In those areas, young women in skimpy dresses hang around in dark corners to woo male clients.
A resident, Henry Njokwu, told our correspondent that Ajegunle serves as an enclave to many teenage mothers who engage in prostitution due to poverty and get pregnant.
“They are ready to sleep with any man for food or stipend. They are made vulnerable because they come from poor homes. A good number of them are secondary school dropouts,” he said.
Henry added that many of them were brilliant but had no opportunity for education.
He also said that some among them were guided by their mothers, who are extremely strict and would never allow them to engage in prostitution.
Sade Kilani, a market leader at the popular Boundary Market, said those who reside in Apapa prefer to buy their food items from the ever-busy market.
Although life in the slum is not always pleasant due to some inhuman conditions dwellers grapple with, there are, however, indications that some prominent personalities were raised in such places.
For example, some football stars and musicians of note were raised at Ajegunle.
Anthony Beluchwuku, who runs a bar on Nosamu Street, said Ajegunle had raised many football stars in the country, such as Samson Siasia, Taribo West and a host of others.
“In the music industry, Daddy Showkey, Danfo Drivers, Marvelous Benji and many others also grew up in Ajegunle,” he added.
Outsiders believe that Ajegunle is a home for criminals, but for the residents, it is home for all and there is no place like it.
Kano
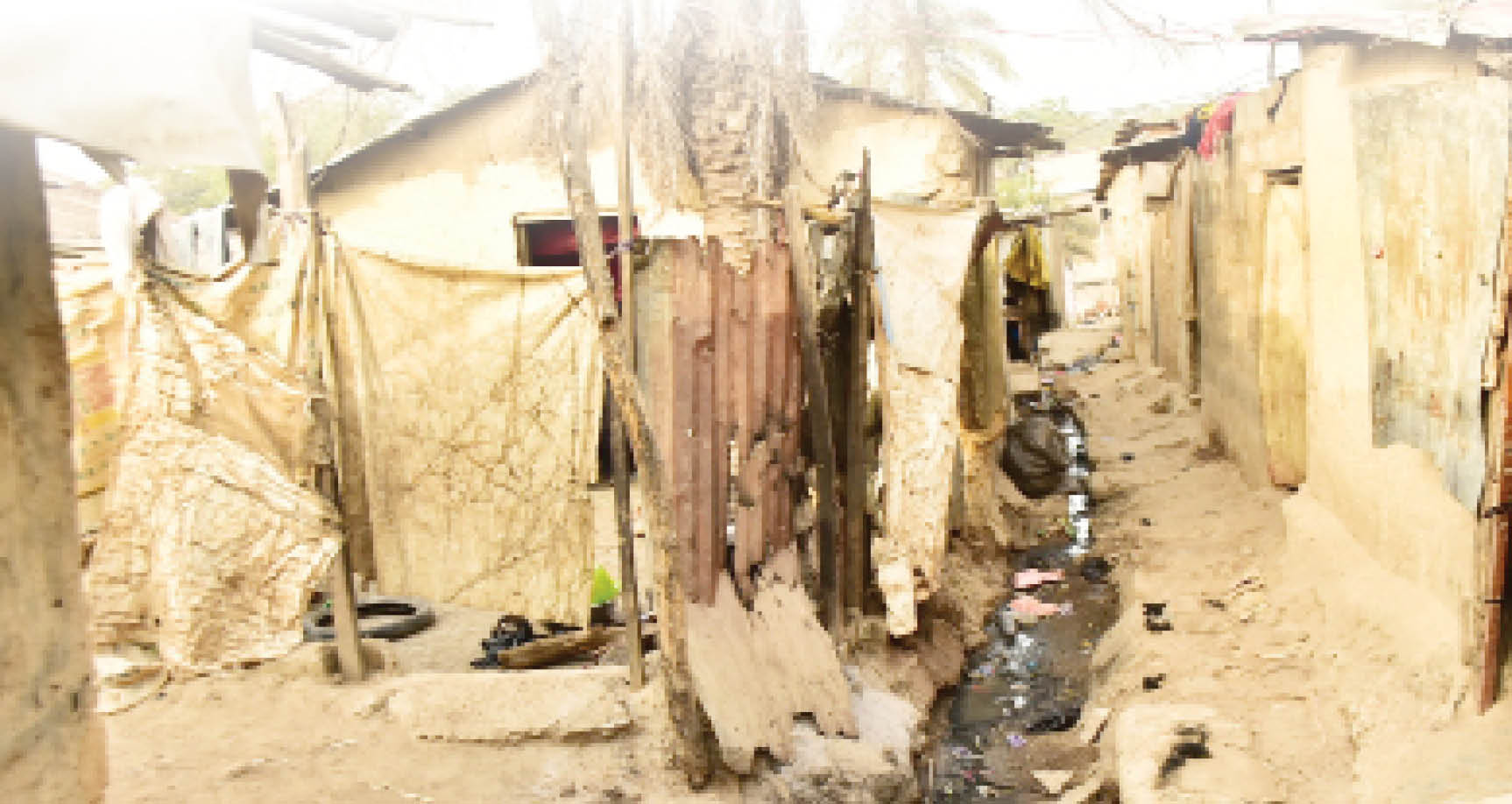
In Kano, life has lost its meaning for some of the people that live in slums due to lack of basic amenities and socioeconomic privileges their urban counterparts enjoy.
When Daily Trust visited some slums in Kano metropolis, which include a section of Kurna Asabe, Jakara and Sanka settlements, all in Dala Local Government Area, as well as Rimin-Kebe in Ungogo Local Government Area, dense population, and lack of infrastructure, poor sanitation and poverty indices were their common challenges.
While many of the inhabitants are trying to cope with the odds, others are calling for gentrification and remodelling for urbanisation and development.
A resident at Burhama in Kurna Asabe, Mubarak Habibu, told our correspondent that child and maternal mortalities were some of the major problems affecting the residents due to lack of health facilities.
“Our area is highly populated. We do not have roads, drainage system, and potable water. We also don’t have health facilities. I have been living in this area for about 28 years and I know how women suffer and die because of lack of health facilities. During the rainy season, flood disaster is our major problem due to poor drainage system.
“Government should focus more on providing adequate health facilities in the area, as well as roads, potable water and a good drainage system to ensure a safe and healthy living environment,” Habibu said.
Abulkadir Muzammil and Anas Ibrahim from Jakara and Sanka areas in Dala Local Government said that poverty, unplanned settlements, as well as the absence of urban physical landscape, were the major challenges faced by residents.
Those who spoke to Daily Trust said most of the settlements were built more than 50 years ago and reduced to slums due to rapid population growth and uncontrolled urban development plan, which also resulted in overdependence on facilities.
They added that the factors accounted for the lack of potable water, health facilities, electricity, civilization and conducive living environment.
“Government should create more opportunities to reduce rural poverty and promote sustainable development. It should also encourage and impose family planning on every household to have an optimum population,” Ibrahim added.
While others are trying to cope with life in slum areas, Habibu Isyaku from Rimin Kebe called for gentrification, the process where the character of a poor urban area is changed by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses, as the only way to enhance their lifestyle.
“It is worrisome to raise a child in such areas with abject poverty and environmental risks. Provision of potable water and road is not the solution to the growing problems faced by people living in slums in urban areas,” he said.
He also called on government to evacuate all the inhabitants to another estate, reconstruct and remodel the slums to fit the current urban architectural layout.

Lokoja
Lokoja, the capital of Kogi State, is supposed to be one of the fastest growing cities in modern Nigeria as it prides itself as the former capital of the country’s colonial administration under Sir Frederick Lord Lugard.
The colonial coloration of Lokoja and its natural gifts of the Rivers Niger and River Benue sourced from Guinea and Cameroon are expected to push the capital city to urbanisation. But findings by our correspondent show that the ancient city has some slums marked by the lack of basic social amenities, especially drinking water, electricity, drainage systems, housing and sanitary facilities.
Our correspondent gathered that residents of Kabawa, Adankolo and Gadumo have more tales of woes because of their proximity to the River Niger than residents of Angwan Kura, Karaworo, Madabo, Rimi, Galilee and Shabayagi .
Residents of the areas have continued to endure poor living standards due to years of neglect, with perennial flood disaster caused by River Niger and River Benue.
Hajiya Shuaibu, a resident of Angwan Kura, lamented that government had neglected the people living in the slums.
Daily Trust gathered that the youths of the areas had, a couple of times, taken to the streets to protest poor living conditions of the people, particularly the lack of electricity and drinkable water.
“We don’t always enjoy regular power supply in Kabawa. Unfortunately, the distribution company keeps increasing the bills monthly. We are paying for service not given to us. This is systemic robbery in our modern generation,” an angry resident of Kabawa, who preferred to be called Abubakar, lamented recently during a protest in Lokoja.
Another resident, Abubakar Sani, said Kabawa lacked government presence, especially basic amenities, such as water, electricity, drainages and good roads.
He lamented that after campaign promises and election, politicians never get back to bring development to the people, making them to remain in perpetual impoverishment.
Shehu Aminu, a tailor who resides in the Madabo area of Lokoja, said scarcity of water was the biggest challenge facing the people. He called on the government to come to their aid.
Owerri
Slums are growing by the day in Owerri, the capital of Imo State, once regarded as the cleanest city east of Niger. In the heart of the ancient city, popularly known as Owerri Nchi Use, the sight of a slum presents a shocking discovery.
Just behind the popular Douglas Road lies a neighbourhood that can be described as a slum bereft of basic amenities.
Chukwu, one of the residents, told our correspondent that he had been living there for a long time and feels nice despite government negligence.
“In fact, I grew up to find myself in this neighbourhood. My parents engaged in buying scraps of metals of all types. From here, they are loaded and transported to places as far as northern states,” he said.
On how he feels living in such an environment, Chukwu said he had gotten used to it.
“Ask anyone living here, we feel as happy as anyone living in any highbrow area. We eke out our living here and go out as everyone else to have fun outside our environment. We also feel safe here.
Another resident who identified himself as Emeka, however, feels the people at the place are neglected by the government. He said, “Here, we provide everything for ourselves, including electricity. Although this place is at the heart of the town, we are in a world of our own.”
Abuja
For people not familiar with the geography of the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), they would never know that some villages and slums exist in the midst of the intimidating opulence of the city.
Our reporter who visited Utako village, a slum around popular Berger Roundabout on Friday night could hardly breathe whilst wandering within the densely populated slum area as stern smells were emanating from the minor gutters erected amidst tiny houses.
Alhaji Rabiu Maigwanjo, 50, who spent more than 20 years in Utako village, notwithstanding the filthy and other abominable things in the slum, said he is living comfortably.
“In my apartment, we have a fan and a restroom. These are the basic amenities found even in the city centre. Of course the surrounding areas are somewhat filthy and therefore people are prone to malaria because of the presence of mosquitoes in the environment,” he said.
George, who works as private security with a private organisation in the Utako area of the city, said he is only managing what life offers.
He said, “I am living in a tiny room where I barely stretch out my legs while sleeping. There is no bath and rest room; it is just a room with no kitchen and no corridor. Though, it is connected with electricity but no tap water inside. Many times, if I am to ease myself in the night, I go to a private restroom where one pays 50 naira. But most times I bathe and ease myself at my place of work because it is not from here.”
Sabo, who also works with a private organization in Jabi area, said during summer time, many people had to sleep outside because of heat and lack of good ventilation in the rooms.
“We buy water from vendors. A jerry can cost between N30 and N50.
“The food is a bit cheaper here than in the city as you can eat to your satisfaction with N300 only. Some people from the city centre do come here and buy food stuff because it is not as expensive as in the city,” he said.
He said the settlement is also inhabited by women of easy virtue who host drunkards, robbers and touts.
Jabi Daki Biyu is a slum located in the fringes of Jabi District but seems to accommodate more than half of the district’s population.
The road leading to Daki Biyu from Obafemi Awolowo Way is well paved but the moment you leave the high rise and luxury buildings behind, the road also ends as another stretch of dirt road snaking around mud shanties begins.
Driving into this settlement, one is greeted with the stench of leaking sewage. Shanties built with corrugated iron sheets or mud serve as shops, restaurants, or homes.
Little children were seen in ragged clothes playing in the dust while the local women were also seen in their usual way of carrying heavy items such as wood and basins of yam on their backs.
Shanty towns like Daki Biyu are not usually far away from the city centre. Some of them located in the heart of the city are poverty-stricken and hidden in shadows, away from the glitz and glamour of the nation’s capital. Yet, they remain a haven for those who desire to live in Abuja.
A resident who gave his name as Musa and runs a provision store told our reporter that having lived in Daki Biyu for some time, he feels normal.
He appealed to the government to come to their aid and make it affordable for everyone in that community.
Another resident, Onyekachukwu Obi, said the slum is also a haven for criminals who attack residents during the day and at night.
“I have been residing in Daki Biyu since 2016. There is no month we don’t have cases of stealing,” he said.
Obi said in order to arrest the situation, the residents organized a vigilante, but yet the problem persists. He called on the relevant authorities to come to their rescue.
Gishiri, another slum is a stone-throw to the highbrow Maitama District in the FCT. People living in the area have been battling with acute water shortages and other necessities.
Suleiman Abdulmalik, an industrial cleaner, said, “Even though I have a tap in my house, it can take two to three months before we get water”.
The community is also lacking a functioning primary healthcare.
“My wife lost her baby because she could not access antenatal,” he said.
Unplanned settlements worrisome – Experts
Uncontrolled and unplanned settlements in Nigerian urban cities have remained one of the challenges affecting urban development in most states.
A human rights activist and the executive director, Conscience for Human Rights and Conflict Resolution (CHRCR), Idris Abdul, called on the government to give local government councils full autonomy and allow them function statutorily to enhance good living conditions in the slums.
He also said local governments should be given the free hand to construct drainages, culverts and markets to alleviate the plights of the people living in areas classified as slums.
Kenneth James, a town planner, said it is not too late to get it right and give the people living in slums a sense of belonging.
“The population will continue to grow and therefore, those in position of responsibility must face the challenge.
“There should be a deliberate attention in providing water, roads and drainages for the poor. The reason we are not getting it right is because governments at all levels renege in their responsibilities,” he said.
Clement Adeyi, Dalhatu Liman & Seun Adeuyi (Abuja), Eugene Agha (Lagos), Usman Bello Balarabe (Kano), Tijani Labaran (Lokoja) & Jude Owuamanam (Owerri)

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.