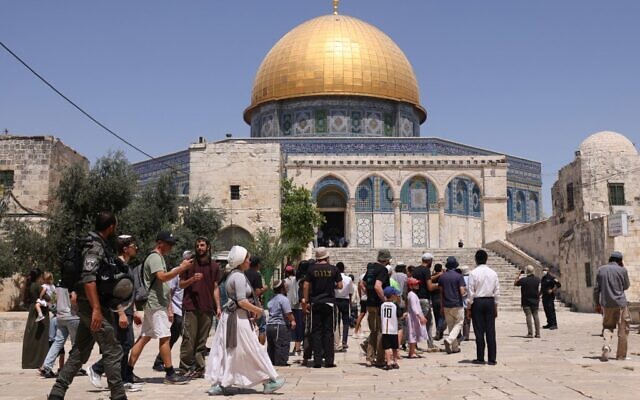
Muslim authorities are outraged over a ruling by a local Israeli court in favour of a Jewish man who prayed quietly at a contested Jerusalem holy site, denouncing the decision Thursday as an infraction against the fragile status quo governing the Al-Aqsa mosque.
The compound, which is the third holiest site in Islam and the holiest site for Jews, is referred to as the Temple Mount by Jews because it is believed to be the location of the ancient Jewish temples. It is a flashpoint in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, helping trigger a recent 11-day burst of fighting in May.
Jews are informally banned from praying there, and the ruling from a magistrate court in Jerusalem was regarding a Jewish man who had been banned from the site for 15 days after Israeli police caught him quietly praying on the ground. The ban was lifted several days early because the man “like many others, prays on a daily basis on the Temple Mount.”
The Islamic endowment that oversees Al-Aqsa called the ruling a “flagrant violation,”and a “clear provocation” for Muslims worldwide. Noting that the man prayed quietly and privately, the ruling said “this activity by itself is not enough to violate the police instructions.”
Under a longstanding but informal arrangement known as the status quo, Jews are allowed to visit the site but not pray there.
The agreement has broken down in recent years as large groups of Jews, including hard-line religious nationalists, have regularly visited and prayed at the site. The Israeli government said it is committed to maintaining the status quo.
The Palestinians and neighbouring Jordan, which serves as the custodian of the holy site, fear that Israel plans to eventually take over the compound or partition it — as it did with a similarly contested holy site in Hebron, in the Israeli-occupied West Bank.
Friday prayers at the mosque are regularly attended by tens of thousands of Palestinians, and are sometimes followed by protests and clashes with Israeli police. A provocative visit by a right-wing Israeli politician in 2000 helped ignite the second Palestinian intifada, or uprising.

 Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.
Join Daily Trust WhatsApp Community For Quick Access To News and Happenings Around You.